Oral isotretinoin for acne vulgaris side effects on the ocular surface: Hyaluronic acid and galacto-xyloglucan as treatment for dry eye disease signs and symptoms
- PMID: 35935781
- PMCID: PMC9353322
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.959165
Oral isotretinoin for acne vulgaris side effects on the ocular surface: Hyaluronic acid and galacto-xyloglucan as treatment for dry eye disease signs and symptoms
Abstract
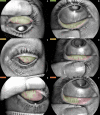
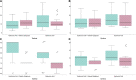
The purpose was to assess the efficacy of 0.4% hyaluronic acid and 0.2% galacto-xyloglucan on the subjective symptoms of dry eye disease and invasive and non-invasive tear film signs in oral isotretinoin for acne vulgaris treatment. A prospective, longitudinal, single-blind, clinical study was performed in oral isotretinoin for the acne vulgaris consumer population. Subjective dry eye disease questionnaires and invasive and non-invasive tear film assessments were reported prior to and after 6 weeks of hyaluronic acid with galacto-xyloglucan (HA-GX) treatment vs. hyaluronic acid alone (HA). Participants in the HA-GX group reported a higher decrease in the ocular surface disease index (17.01 ± 11.36 score points) compared to the variation in participants in the HA group (11.61 ± 11.18 score points). Standard patient evaluation of eye dryness also decreased more in participants in the HA-GX group (4.06 ± 5.50 score points) than in participants who received HA alone (0.70 ± 3.16). Regarding non-invasive break-up time (NIBUT), participants in the HA-GX group first NIBUT achieved an increase of 1.75 ± 1.16 s while participants in the HA-alone group demonstrated an increase of only 0.54 ± 1.01 s. The HA-GX group mean NIBUT increased by of 3.72 ± 5.69 s; however, the value for the HA-alone group was 2.19 ± 5.26 s. Hyaluronic acid in combination with galacto-xyloglucan significantly decreased limbal and bulbar conjunctival redness classification and SPEED test outcomes. The inclusion of galacto-xyloglucan also increased BUT and mean NIBUT values compared to those obtained with hyaluronic acid alone.
Keywords: acne vulgaris; dry eye disease; eyedrops; galacto xyloglucan; hyaluronic acid; isotretinoin; tear film.
Copyright © 2022 Sánchez-González, De-Hita-Cantalejo, Martínez-Lara and Sánchez-González.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures