Nitidine Chloride Alleviates Inflammation and Cellular Senescence in Murine Osteoarthritis Through Scavenging ROS
- PMID: 35935815
- PMCID: PMC9353946
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.919940
Nitidine Chloride Alleviates Inflammation and Cellular Senescence in Murine Osteoarthritis Through Scavenging ROS
Abstract
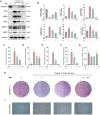
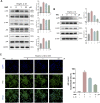
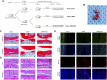
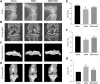
Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the most common chronic musculoskeletal disorder worldwide, representing a major source of disability, pain and socioeconomic burden. Yet the effective pharmaceutical treatments applied in the clinical works are merely symptomatic management with uncertainty around their long-term safety and efficacy, namely no drugs currently are capable of modulating the biological progression of OA. Here, we identified the potent anti-inflammatory as well as anti-oxidative properties of Nitidine Chloride (NitC), a bioactive phytochemical alkaloid extracted from natural herbs, in IL-1β-treated rat articular chondrocytes (RACs), LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 and rat osteoarthritic models in vivo. We demonstrated NitC remarkably inhibited the production of inflammatory mediators including COX2 and iNOS, suppressed the activation of MAPK and NF-κB cell signaling pathway and reduced the expression of extracellular matrix (ECM) degrading enzymes including MMP3, MMP9 and MMP13 in IL-1β-treated RACs. Several emerging bioinformatics tools were performed to predict the underlying mechanism, the result of which indicated the potential reactive oxygen species (ROS) clearance potential of NitC. Further, NitC exhibited its anti-oxidative potential through ameliorating cellular senescence in IL-1β-treated RACs and decreasing NLRP3 inflammasomes activation in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 via scavenging ROS. Additionally, X-ray, micro-CT and other experiments in vivo demonstrated that intra-articular injection of NitC significantly alleviated the cartilage erosion, ECM degradation and subchondral alterations in OA progression. In conclusion, the present study reported the potent anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative potential of NitC in OA biological process, providing a promising therapeutic agent for OA management.
Keywords: MAPK; NF-κB; NLRP3 inflammasome; ROS; nitidine chloride; osteoarthritis; senescence.
Copyright © 2022 Lin, Ge, Tang, He, Moqbel, Xu, Ma, Zhou, Ran and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

