Class IIa histone deacetylase inhibition ameliorates acute kidney injury by suppressing renal tubular cell apoptosis and enhancing autophagy and proliferation
- PMID: 35935816
- PMCID: PMC9354984
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.946192
Class IIa histone deacetylase inhibition ameliorates acute kidney injury by suppressing renal tubular cell apoptosis and enhancing autophagy and proliferation
Abstract
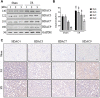
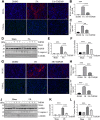
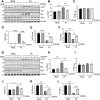
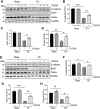
Expression and function of histone deacetylases (HDACs) vary with cell types and pathological conditions. Our recent studies showed that pharmacological targeting class IIa HDACs attenuated renal fibrosis, but the effect of class IIa HDAC inhibition on acute kidney injury (AKI) remains unknown. In this study, we found that four class IIa HDACs (4, 5, 7, 9) were highly expressed in the kidney of folic acid (FA) and ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced AKI in mice. Administration of TMP269, a potent and selective class IIa HDAC inhibitor, improved renal function and reduced tubular cell injury and apoptosis, with concomitant suppression of HDAC4 and elevation of acetyl-histone H3. Mechanistical studies showed that TMP269 treatment inhibited FA and I/R-induced caspase-3 cleavage, Bax expression and p53 phosphorylation. Conversely, TMP269 administration preserved expression of E-cadherin, BMP7, Klotho and Bcl-2 in injured kidneys. Moreover, TMP269 was effective in promoting cellular autophagy as indicated by increased expression of Atg7, beclin-1, and LC3II, and promoted renal tubular cell proliferation as shown by increased number of proliferating cell nuclear antigen-positive cells and expression of cyclin E. Finally, blocking class IIa HDACs inhibited FA-and I/R-induced phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2, and p38, two signaling pathways associated with the pathogenesis of AKI. Collectively, these results suggest that pharmacological inhibition of class IIa HDACs protects against AKI through ameliorating apoptosis, enhancing autophagy and promoting proliferation of renal tubular cells by targeting multiple signaling pathways.
Keywords: TMP269; acute kidney injury; apoptosis; autophagy; class IIa histone deacetylases; folic acid; ischemia/reperfusion; renal tubular cells.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Yu, Shen, Cui, Liu and Zhuang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

