Recent Advance in Tumor Microenvironment-Based Stimuli-Responsive Nanoscale Drug Delivery and Imaging Platform
- PMID: 35935835
- PMCID: PMC9354407
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.929854
Recent Advance in Tumor Microenvironment-Based Stimuli-Responsive Nanoscale Drug Delivery and Imaging Platform
Abstract
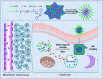
The tumor microenvironment (TME) plays an important role in the development, progression, and metastasis of cancer, and the extremely crucial feature is hypoxic and acidic. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), extracellular matrix (ECM), mesenchymal cells, blood vessels, and interstitial fluid are widely recognized as fundamentally crucial hallmarks for TME. As nanotechnology briskly boomed, the nanoscale drug delivery and imaging platform (NDDIP) emerged and has attracted intensive attention. Based on main characteristics of TME, NDDIP can be classified into pH-sensitive delivery and imaging platforms, enzyme-sensitive delivery and imaging platforms, thermo-sensitive delivery and imaging platforms, redox-sensitive delivery and imaging platforms, and light-sensitive delivery and imaging platforms. Furthermore, imageology is one of the significant procedures for disease detection, image-guided drug delivery, and efficacy assessment, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), ultrasound (US), and fluorescence imaging. Therefore, the stimuli-responsive NDDIP will be a versatile and practicable tumor disease diagnostic procedure and efficacy evaluation tool. In this review article, we mainly introduce the characteristics of TME and summarize the progress of multitudinous NDDIP as well as their applications.
Keywords: TME; cancer therapy; imaging platform; nanomaterials; stimuli-responsive nanoscale drug delivery.
Copyright © 2022 Cui, Liu, Pang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The application of nanoparticles in cancer immunotherapy: Targeting tumor microenvironment.Bioact Mater. 2020 Dec 26;6(7):1973-1987. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.12.010. eCollection 2021 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 33426371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Nanotheranostic Agents for Tumor Microenvironment-Responsive Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 22;13:924131. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.924131. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35814250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress in Stimuli-Responsive Intelligent Nano Scale Drug Delivery Systems: A Special Focus Towards pH-Sensitive Systems.Curr Drug Targets. 2021;22(8):947-966. doi: 10.2174/1389450122999210128180058. Curr Drug Targets. 2021. PMID: 33511953 Review.
-
Exploiting a New Approach to Destroy the Barrier of Tumor Microenvironment: Nano-Architecture Delivery Systems.Molecules. 2021 May 5;26(9):2703. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092703. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34062992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-Mediated Targeted Drug Delivery to Remodel Tumor Microenvironment for Cancer Therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Aug 25;16:5811-5829. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S321416. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34471353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Revealing tumor cells and tissues with high selectivity through folic acid-targeted nanofluorescence probes responsive to acidic microenvironments.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 12;14:1404148. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1404148. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38933449 Free PMC article.
-
Gold Nanocage-Based Multifunctional Nanosensitizers for Programmed Photothermal /Radiation/Chemical Coordinated Therapy Guided by FL/MR/PA Multimodal Imaging.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Dec 5;18:7237-7255. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S436931. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 38076731 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor microenvironment-responsive nanoformulations for breast cancer.Discov Nano. 2024 Dec 21;19(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s11671-024-04122-5. Discov Nano. 2024. PMID: 39708097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Combined with Nanoformulation to Advance Therapeutic Technologies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 21;16(12):1634. doi: 10.3390/ph16121634. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139761 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aminu N., Bello I., Umar N. M., Tanko N., Aminu A., Audu M. M. (2020). The Influence of Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery Systems in Drug Therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 60, 101961. [J]. 10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101961 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

