Fluorescent Tracers for In Vivo Imaging of Lymphatic Targets
- PMID: 35935839
- PMCID: PMC9355481
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.952581
Fluorescent Tracers for In Vivo Imaging of Lymphatic Targets
Abstract
The lymphatic system continues to gain importance in a range of conditions, and therefore, imaging of lymphatic vessels is becoming more widespread for research, diagnosis, and treatment. Fluorescent lymphatic imaging offers advantages over other methods in that it is affordable, has higher resolution, and does not require radiation exposure. However, because the lymphatic system is a one-way drainage system, the successful delivery of fluorescent tracers to lymphatic vessels represents a unique challenge. Each fluorescent tracer used for lymphatic imaging has distinct characteristics, including size, shape, charge, weight, conjugates, excitation/emission wavelength, stability, and quantum yield. These characteristics in combination with the properties of the target tissue affect the uptake of the dye into lymphatic vessels and the fluorescence quality. Here, we review the characteristics of visible wavelength and near-infrared fluorescent tracers used for in vivo lymphatic imaging and describe the various techniques used to specifically target them to lymphatic vessels for high-quality lymphatic imaging in both clinical and pre-clinical applications. We also discuss potential areas of future research to improve the lymphatic fluorescent tracer design.
Keywords: fluorescent imaging; fluorophore; in vivo; lymph node; lymphatic.
Copyright © 2022 Russell, Velivolu, Maldonado Zimbrón, Hong, Kavianinia, Hickey, Windsor and Phillips.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor SH declared a past co-authorship with authors JH, AP, JW.
Figures
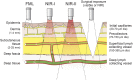

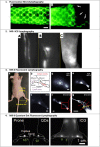
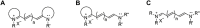
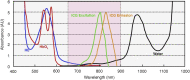
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

