Caper (Capparis spinosa L.): An Updated Review on Its Phytochemistry, Nutritional Value, Traditional Uses, and Therapeutic Potential
- PMID: 35935860
- PMCID: PMC9353632
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.878749
Caper (Capparis spinosa L.): An Updated Review on Its Phytochemistry, Nutritional Value, Traditional Uses, and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
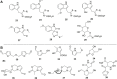
Caper (Capparis spinosa L.) is a perennial shrub of the family Capparaceae, endemic to circum-Mediterranean countries. Caper carries a renowned nutritional value, especially in terms of vitamins and antioxidants related to the occurrence of flavonoids, alkaloids, and glucosinolates as main secondary metabolites. Caper extracts have also shown to display antibacterial, antifungal, analgesic, antitumor, hepatoprotective, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects which correlate the uses of the plant in folk medicine against both metabolic and infectious diseases. The present review aims to provide exhaustive phytochemistry and pharmacological properties survey on Caper constituents. Attention has also been given to the nutritional values and traditional uses of main organs to pinpoint research gaps for future investigations on the plant.
Keywords: antidiabetic; caper bush; capparaceae; flavonoids; flinders rose; glucosinolates; hepatoprotective; indoles.
Copyright © 2022 Annaz, Sane, Bitchagno, Ben Bakrim, Drissi, Mahdi, El Bouhssini and Sobeh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

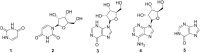





Similar articles
-
Phytochemistry, Biological Activities, Therapeutic Potential, and Socio-Economic Value of the Caper Bush (Capparis Spinosa L.).Chem Biodivers. 2022 Oct;19(10):e202200300. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202200300. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Chem Biodivers. 2022. PMID: 36064949 Review.
-
Capparis spinosa L. as a potential source of nutrition and its health benefits in foods: A comprehensive review of its phytochemistry, bioactivities, safety, and application.Food Chem. 2023 May 30;409:135258. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135258. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 36587515 Review.
-
Caper bush (Capparis spinosa L.) bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity as affected by adaptation to harsh soils.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 7;15(1):11893. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97298-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40195406 Free PMC article.
-
Antidiabetic properties of Capparis spinosa L. and its components.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Aug;92:293-302. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.082. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28551550 Review.
-
The Capparis spinosa var. herbacea genome provides the first genomic instrument for a diversity and evolution study of the Capparaceae family.Gigascience. 2022 Oct 30;11:giac106. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giac106. Gigascience. 2022. PMID: 36310248 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Ethnopharmacological Analysis of Medicinal Plants in the UAE: Lawsonia inermis, Nigella sativa, Ziziphus spina-christi, Allium cepa, Allium sativum, Cymbopogon schoenanthus, Matricaria aurea, Phoenix dactylifera, Portulaca oleracea, Reichardia tingitana, Salvadora persica, Solanum lycopersicum, Trigonella foenum-graecum, Withania somnifera, and Ziziphus lotus.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 23;17(3):411. doi: 10.3390/nu17030411. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39940269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of drying methods on phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of Capparis spinosa L. fruits.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jan 31;25(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06110-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39891043 Free PMC article.
-
Spice components as modulating agents of P-glycoprotein - An in silico study.Indian J Pharmacol. 2024 May 1;56(3):214-219. doi: 10.4103/ijp.ijp_299_23. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Indian J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39078186 Free PMC article.
-
Functional foods in Mediterranean diet: exploring the functional features of vegetable case-studies obtained also by biotechnological approaches.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024 Oct 16;36(1):208. doi: 10.1007/s40520-024-02860-1. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024. PMID: 39412623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant activity and selective cytotoxicity in HCT-116 and WI-38 cell lines of LC-MS/MS profiled extract from Capparis spinosa L.Front Chem. 2025 Apr 10;13:1540174. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1540174. eCollection 2025. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 40276802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd Al-Majeed M. I., Al-Ghizawi G. J., Dawwas B. H. A. A. A., Al-Maliki M. (2016). Isolation and Identification of Alkaloidic Extract of Capparis spinosaL Buds and Study of its Cytoxicity and Antibacterial Activity. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 6 6.
-
- Adwan G. M., Omar G. I. (2021). Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity and Genotoxic Potential of Capparis Spinosa (L.) Plant Extracts. Microbiol. Res. J. Int. 31 (1), 48–57. 10.9734/mrji/2021/v31i130297 - DOI
-
- Afsharypuor S., Jeiran K., Jazy A. A. (1998). First Investigation of the Flavour Profiles of the Leaf, Ripe Fruit and Root of Capparis Spinosa Var. Mucronifolia from Iran. Pharm. Acta Helvetiae 72 (5), 307–309. 10.1016/s0031-6865(97)00023-x - DOI
-
- Aichour R., Benzidane N., Arrar L., Charef N., Baghiani A. (2018). Hepatoprotective and Anti-inflammatory Activities of Algerian Capparis Spinosa. L. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 25 (3), 1–12. 10.9734/arrb/2018/40410 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

