Therapeutic application of quercetin in aging-related diseases: SIRT1 as a potential mechanism
- PMID: 35935939
- PMCID: PMC9355713
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.943321
Therapeutic application of quercetin in aging-related diseases: SIRT1 as a potential mechanism
Abstract
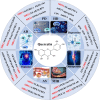
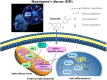
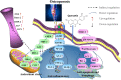
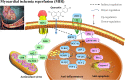
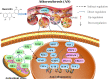
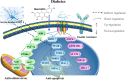
Quercetin, a naturally non-toxic flavonoid within the safe dose range with antioxidant, anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory properties, plays an important role in the treatment of aging-related diseases. Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), a member of NAD+-dependent deacetylase enzyme family, is extensively explored as a potential therapeutic target for attenuating aging-induced disorders. SIRT1 possess beneficial effects against aging-related diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), Huntington's disease (HD), Depression, Osteoporosis, Myocardial ischemia (M/I) and reperfusion (MI/R), Atherosclerosis (AS), and Diabetes. Previous studies have reported that aging increases tissue susceptibility, whereas, SIRT1 regulates cellular senescence and multiple aging-related cellular processes, including SIRT1/Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 and SIRTI/PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β mediated oxidative stress, SIRT1/NF-κB and SIRT1/NLRP3 regulated inflammatory response, SIRT1/PGC1α/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP and SIRT1/PKD1/CREB controlled phosphorylation, SIRT1-PINK1-Parkin mediated mitochondrial damage, SIRT1/FoxO mediated autophagy, and SIRT1/FoxG1/CREB/BDNF/Trkβ-catenin mediated neuroprotective effects. In this review, we summarized the role of SIRT1 in the improvement of the attenuation effect of quercetin on aging-related diseases and the relationship between relevant signaling pathways regulated by SIRT1. Moreover, the functional regulation of quercetin in aging-related markers such as oxidative stress, inflammatory response, mitochondrial function, autophagy and apoptosis through SIRT1 was discussed. Finally, the prospects of an extracellular vesicles (EVs) as quercetin loading and delivery, and SIRT1-mediated EVs as signal carriers for treating aging-related diseases, as well as discussed the ferroptosis alleviation effects of quercetin to protect against aging-related disease via activating SIRT1. Generally, SIRT1 may serve as a promising therapeutic target in the treatment of aging-related diseases via inhibiting oxidative stress, reducing inflammatory responses, and restoring mitochondrial dysfunction.
Keywords: aging-related diseases; inflammatory response; mitochondrial dysfunction; oxidative stress; quercetin; sirtuin 1.
Copyright © 2022 Cui, Zhao, Amevor, Du, Wang, Li, Shu, Tian and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Shaping the Nrf2-ARE-related pathways in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.Ageing Res Rev. 2019 Sep;54:100942. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2019.100942. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Ageing Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 31415806 Review.
-
Oroxylin A ameliorates ultraviolet radiation-induced premature skin aging by regulating oxidative stress via the Sirt1 pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Feb;171:116110. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.116110. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38198955
-
Galangin Reverses H2O2-Induced Dermal Fibroblast Senescence via SIRT1-PGC-1α/Nrf2 Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 26;23(3):1387. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031387. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163314 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperoside, a natural flavonoid compound, attenuates Triptolide-induced testicular damage by activating the Keap1-Nrf2 and SIRT1-PGC1α signalling pathway.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;74(7):985-995. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgac011. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35325199
-
Traversing through the cell signaling pathways of neuroprotection by betanin: therapeutic relevance to Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease.Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Mar;38(3):805-817. doi: 10.1007/s11011-023-01177-8. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Metab Brain Dis. 2023. PMID: 36745251 Review.
Cited by
-
Qianggu concentrate: unlocking bone protection power via antioxidative SIRT1/NRF2/HO-1 pathways in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 8;15:1426767. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1426767. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39175549 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Modulates Ferroptosis via the SIRT1/Nrf-2/HO-1 Pathway and Attenuates Cartilage Destruction in an Osteoarthritis Rat Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 7;25(13):7461. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137461. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000568 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated network pharmacology and experimental validation to explore the potential pharmacological mechanism of Qihuang Granule and its main ingredients in regulating ferroptosis in AMD.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Nov 21;23(1):420. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04205-3. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37990310 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Activity of Flavonoid Quercetin and Its Therapeutic Potential in Testicular Injury.Nutrients. 2023 May 8;15(9):2231. doi: 10.3390/nu15092231. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Ferroptosis Involvement in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Pathogenesis: Neuroprotective Activity of Polyphenols.Molecules. 2025 Mar 8;30(6):1211. doi: 10.3390/molecules30061211. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40141987 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

