Hexavalent Chromium Exposure Induces Intestinal Barrier Damage via Activation of the NF-κB Signaling Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome in Ducks
- PMID: 35935959
- PMCID: PMC9353580
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.952639
Hexavalent Chromium Exposure Induces Intestinal Barrier Damage via Activation of the NF-κB Signaling Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome in Ducks
Abstract
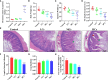
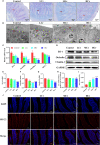
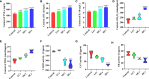
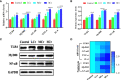
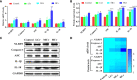
Hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] is a dangerous heavy metal which can impair the gastrointestinal system in various species; however, the processes behind Cr(VI)-induced intestinal barrier damage are unknown. Forty-eight healthy 1-day-old ducks were stochastically assigned to four groups and fed a basal ration containing various Cr(VI) dosages for 49 days. Results of the study suggested that Cr(VI) exposure could significantly increase the content of Cr(VI) in the jejunum, increase the level of diamine oxidase (DAO) in serum, affect the production performance, cause histological abnormalities (shortening of the intestinal villi, deepening of the crypt depth, reduction and fragmentation of microvilli) and significantly reduced the mRNA levels of intestinal barrier-related genes (ZO-1, occludin, claudin-1, and MUC2) and protein levels of ZO-1, occludin, cand laudin-1, resulting in intestinal barrier damage. Furthermore, Cr(VI) intake could increase the contents of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and malondialdehyde (MDA), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and interleukin-18 (IL-18) but decrease the activities of total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione reductase (GR), as well as up-regulate the mRNA levels of TLR4, MyD88, NF-κB, TNFα, IL-6, NLRP3, caspase-1, ASC, IL-1β, and IL-18 and protein levels of TLR4, MyD88, NF-κB, NLRP3, caspase-1, ASC, IL-1β, and IL-18 in the jejunum. In conclusion, Cr(VI) could cause intestinal oxidative damage and inflammation in duck jejunum by activating the NF-κB signaling pathway and the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Keywords: NF-κB; NLRP3; duck; hexavalent chromium; intestinal barrier.
Copyright © 2022 Xing, Yang, Lin, Shan, Yi, Ali, Zhu, Wang, Zhang, Zhuang, Cao and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Berberine on Activation of TLR4-NFκB Signaling Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome in Patients with Gout.Chin J Integr Med. 2023 Jan;29(1):10-18. doi: 10.1007/s11655-022-3720-7. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Chin J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 36125615
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuated Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Early Brain Injury in Rats by Suppressing Inflammatory Response: Possible Involvement of NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jul;53(5):3462-3476. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9242-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26091790
-
Apigenin and apigenin-7, 4'-O-dioctanoate protect against acrolein-aggravated inflammation via inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and HMGB1/MYD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC).Food Chem Toxicol. 2022 Oct;168:113400. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.113400. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Food Chem Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36055550
-
Inflammatory effects of hexavalent chromium in the lung: A comprehensive review.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 15;455:116265. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2022.116265. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36208701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of the mode of action underlying development of rodent small intestinal tumors following oral exposure to hexavalent chromium and relevance to humans.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2013 Mar;43(3):244-74. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2013.768596. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23445218 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hexavalent-Chromium-Induced Disruption of Mitochondrial Dynamics and Apoptosis in the Liver via the AMPK-PGC-1α Pathway in Ducks.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 8;24(24):17241. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417241. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139070 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting gut microbiota for diabetic nephropathy treatment: probiotics, dietary interventions, and fecal microbiota transplantation.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 30;16:1621968. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1621968. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40661744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Hexavalent Chromium-Induced Necroptosis, Pyroptosis, and Ferroptosis.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 May;203(5):2619-2635. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04376-1. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 39287767 Review.
-
Hexavalent chromium induces ferroptosis in small intestinal tissue of broilers through GPX4/HMGB1/p38-MAPK pathway.Poult Sci. 2025 Apr;104(4):104978. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104978. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40048981 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of IgY Embedded in W/O/W Emulsion on LPS Enteritis-Induced Colonic Injury in Mice.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 3;16(19):3361. doi: 10.3390/nu16193361. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39408328 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

