RNA m6A modification orchestrates the rhythm of immune cell development from hematopoietic stem cells to T and B cells
- PMID: 35935968
- PMCID: PMC9354743
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.839291
RNA m6A modification orchestrates the rhythm of immune cell development from hematopoietic stem cells to T and B cells
Abstract
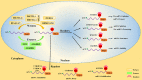
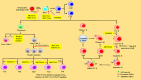
RNA, one of the major building blocks of the cell, participates in many essential life processes. RNA stability is well-established to be closely related to various RNA modifications. To date, hundreds of different RNA modifications have been identified. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is one of the most important RNA modifications in mammalian cells. An increasing body of evidence from recently published studies suggests that m6A modification is a novel immune system regulator of the generation and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and immune cells. In this review, we introduce the process and relevant regulatory mechanisms of m6A modification; summarize recent findings of m6A in controlling HSC generation and self-renewal, and the development and differentiation of T and B lymphocytes from HSCs; and discuss the potential mechanisms involved.
Keywords: B cell; N6-methyladenosine; RNA; T cell; hematopoietic stem cell.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Xu, Zhang, Ye, Cai and Shao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
One Stone, Two Birds: N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in Leukemia Stem Cells and the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 2;13:912526. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.912526. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35720276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of RNA epigenetic modification in normal and malignant hematopoiesis.Curr Stem Cell Rep. 2020 Dec;6(4):144-155. doi: 10.1007/s40778-020-00178-y. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Curr Stem Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 33777659 Free PMC article.
-
Lrp5 and Lrp6 are required for maintaining self-renewal and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells.FASEB J. 2019 Apr;33(4):5615-5625. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802072R. Epub 2019 Jan 22. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30668923 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of m6A reader Ythdf2 promotes hematopoietic stem cell expansion.Cell Res. 2018 Sep;28(9):904-917. doi: 10.1038/s41422-018-0072-0. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 30065315 Free PMC article.
-
M6 A modification: A mechanism for protecting hematopoietic development in mammals.Cell Biol Int. 2021 Jan;45(1):58-60. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11471. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Cell Biol Int. 2021. PMID: 32997376 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of RNA methylation in tumor immunity and its potential in immunotherapy.Mol Cancer. 2024 Jun 20;23(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02041-8. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38902779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methylation of T and B Lymphocytes in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024 Jun;66(3):401-422. doi: 10.1007/s12016-024-09003-4. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39207646 Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in inflammation: a bibliometric analysis and literature review.PeerJ. 2024 Dec 13;12:e18645. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18645. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39686999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The YTH domain-containing protein family: Emerging players in immunomodulation and tumour immunotherapy targets.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Aug;14(8):e1784. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1784. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39135292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Current Detection Methods for RNA Methylation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 7;25(6):3098. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063098. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542072 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

