Sildenafil, a Type-5 Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor, Fails to Reverse Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell-Mediated T Cell Suppression in Cells Isolated From Tuberculosis Patients
- PMID: 35935981
- PMCID: PMC9353143
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.883886
Sildenafil, a Type-5 Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor, Fails to Reverse Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell-Mediated T Cell Suppression in Cells Isolated From Tuberculosis Patients
Abstract
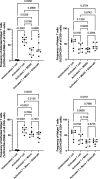
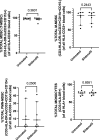
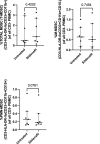
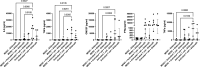
Successful TB treatment is hampered by increasing resistance to the two most effective first-line anti-TB drugs, namely isoniazid and rifampicin, thus innovative therapies focused on host processes, termed host-directed therapies (HDTs), are promising novel approaches for increasing treatment efficacy without inducing drug resistance. We assessed the ability of Sildenafil, a type-5 phosphodiesterase inhibitor, as a repurposed compound, to serve as HDT target, by counteracting the suppressive effects of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) obtained from active TB cases on T-cell responsiveness. We confirm that MDSC suppress non-specific T-cell activation. We also show that Sildenafil treatment fails to reverse the MDSC-mediated suppression of T-cell functions measured here, namely activation and proliferation. The impact of Sildenafil treatment on improved immunity, using the concentration tested here, is likely to be minimal, but further identification and development of MDSC-targeting TB host-directed therapies are warranted.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Sildenafil; host-directed therapies; myeloid-derived suppressor cells; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2022 Leukes, Malherbe, Hiemstra, Kotze, Roos, Keyser, De Swardt, Gutschmidt, Walzl and du Plessis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

