Chemokines in progression, chemoresistance, diagnosis, and prognosis of colorectal cancer
- PMID: 35935996
- PMCID: PMC9353076
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.724139
Chemokines in progression, chemoresistance, diagnosis, and prognosis of colorectal cancer
Abstract
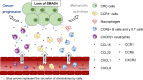
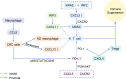
Plenty of factors affect the oncogenesis and progression of colorectal cancer in the tumor microenvironment, including various immune cells, stromal cells, cytokines, and other factors. Chemokine is a member of the cytokine superfamily. It is an indispensable component in the tumor microenvironment. Chemokines play an antitumor or pro-tumor role by recruitment or polarization of recruiting immune cells. Meanwhile, chemokines, as signal molecules, participate in the formation of a cross talk among signaling pathways and non-coding RNAs, which may be involved in promoting tumor progression. In addition, they also function in immune escape. Chemokines are related to drug resistance of tumor cells and may even provide reference for the diagnosis, therapy, and prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer.
Keywords: chemokines; colorectal cancer; immune escape; ncRNAs; signal molecules.
Copyright © 2022 Zou, Lei, Xu, Li, He, Huang, Xu, Tian, Ding and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The functional roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in colorectal cancer progression.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jan;170:116040. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.116040. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38113624 Review.
-
Cytokine- and chemokine-induced inflammatory colorectal tumor microenvironment: Emerging avenue for targeted therapy.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2022 Aug;42(8):689-715. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12295. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35791509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Chemokines in Promoting Colorectal Cancer Invasion/Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Apr 28;17(5):643. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050643. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27136535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond Cell Motility: The Expanding Roles of Chemokines and Their Receptors in Malignancy.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 4;11:952. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00952. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32582148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relationship between chemokines CCL2, CCL3, and CCL4 with the tumor microenvironment and tumor-associated macrophage markers in colorectal cancer.Tumour Biol. 2018 Nov;40(11):1010428318810059. doi: 10.1177/1010428318810059. Tumour Biol. 2018. PMID: 30419802
Cited by
-
CXCL11: A Novel Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer as Metastasis Predictor.Onco Targets Ther. 2025 May 14;18:657-665. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S515119. eCollection 2025. Onco Targets Ther. 2025. PMID: 40386032 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of the chemokine/chemokine receptor axes in the oncobiology of multiple myeloma (MM).Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Mar 12;22(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01544-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38475811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk Between the Nervous System and Colorectal Cancer.Neurosci Bull. 2025 Jan;41(1):93-106. doi: 10.1007/s12264-024-01238-7. Epub 2024 Jun 16. Neurosci Bull. 2025. PMID: 38879846 Review.
-
Chemotherapy-induced macrophage CXCL7 expression drives tumor chemoresistance via the STAT1/PHGDH-serine metabolism axis and SAM paracrine feedback to M2 polarization.Cell Death Dis. 2025 May 14;16(1):379. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07712-y. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40368902 Free PMC article.
-
JAK1 Is a Novel Target of Tumor- and Invasion-Suppressive microRNA 494-5p in Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 20;16(1):24. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010024. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wild C, Weiderpass E, Stewart B. World cancer resport: Cancer research for cancer prevention. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; (2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

