Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease Following COVID-19 Infection in a 7-Year-Old Girl: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 35936128
- PMCID: PMC9351715
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.26540
Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease Following COVID-19 Infection in a 7-Year-Old Girl: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
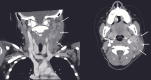
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) symptoms in children are relatively mild and often do not require treatment. Nonetheless, complications caused by the immune response to COVID-19 in children are possible and diverse. We present the case of a 7-year-old girl with persistent fever and lymphadenopathy arising from SARS-CoV-2 infection, diagnosed with Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease (KFD) on lymph node biopsy. KFD is a rare benign disease, clinically characterized by fever and tender cervical lymphadenopathy affecting posterior cervical lymph nodes. We also reviewed six previously reported cases of COVID-19-associated KFD that occurred in school-aged children and compared them with the present case. The clinical course of COVID-19-associated KFD was similar to that of previous reports of KFD with a favorable prognosis. This is the first report of a school-aged child developing KFD following SARS-CoV-2 infection. KFD should be considered when approaching patients with hyperinflammatory states who present with prolonged fever and cervical lymphadenopathy after COVID-19.
Keywords: cervical lymphadenopathy; covid-19; histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis; kikuchi-fujimoto disease; sars-cov-2.
Copyright © 2022, Saito et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Epidemiology of COVID-19 among children in China. Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, Qi X, Jiang F, Jiang Z, Tong S. Pediatrics. 2020;145:0. - PubMed
-
- COVID-19 exposure: a possible association with congenital anomalies and adverse neonatal outcomes. Satnarine T, Kin CML. JMHS. 2022;3:44–48.
-
- Cervical subacute necrotizing lymphadenitis. A new clinicopathological entity. Fujimoto Y, Kojima Y, Yamaguchi K. Naika. 1972;20:920–927.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
