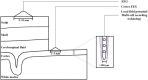
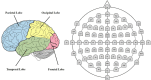
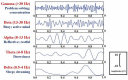
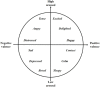
The Application of Electroencephalogram in Driving Safety: Current Status and Future Prospects
- PMID: 35936295
- PMCID: PMC9354986
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.919695
The Application of Electroencephalogram in Driving Safety: Current Status and Future Prospects
Abstract
The driver is one of the most important factors in the safety of the transportation system. The driver's perceptual characteristics are closely related to driving behavior, while electroencephalogram (EEG) as the gold standard for evaluating human perception is non-deceptive. It is essential to study driving characteristics by analyzing the driver's brain activity pattern, effectively acquiring driver perceptual characteristics, creating a direct connection between the driver's brain and external devices, and realizing information interchange. This paper first introduces the theories related to EEG, then reviews the applications of EEG in scenarios such as fatigue driving, distracted driving, and emotional driving. The limitations of existing research have been identified and the prospect of EEG application in future brain-computer interface automotive assisted driving systems have been proposed. This review provides guidance for researchers to use EEG to improve driving safety. It also offers valuable suggestions for future research.
Keywords: distraction driving; electroencephalogram; emotion driving; fatigue driving; traffic safety.
Copyright © 2022 Peng, Xu, Lin, Wang, Xiang, Huang, Zhang and Fan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abhang P. A., Gawali B. W., Mehrotra S. C. (2016). “Proposed EEG/speech-based emotion recognition system: a case study,” in Introduction to EEG- and Speech-Based Emotion Recognition (Amsterdam: Elsevier; ), 127–163. 10.1016/B978-0-12-804490-2.00007-5 - DOI
-
- Acharya J. N., Hani A., Cheek J., Thirumala P., Tsuchida T. N. (2016). American clinical neurophysiology society guideline 2: guidelines for standard electrode position nomenclature. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 33 308–311. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources