Person-Job Misfit: Perceived Overqualification and Counterproductive Work Behavior
- PMID: 35936320
- PMCID: PMC9355648
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.936900
Person-Job Misfit: Perceived Overqualification and Counterproductive Work Behavior
Abstract
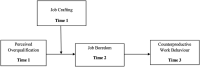
Grounding on person-job fit theory, we examined perceived overqualification relation with counterproductive work behavior (CWB) by identifying job boredom as a mediator and job crafting as a moderator. Hierarchical linear regression and Hayes' PROCESS macro-method were used to assess hypotheses in a three-wave survey of 317 textile sector employees. The findings show that perceived overqualification is positively related with CWBs. This study further examined the mediating function of job boredom and the moderating impact of job crafting in the association between perceived overqualification and CWB. The findings suggest that job crafting moderates the positive relation between perceived overqualification and job boredom and the indirect connection between perceived overqualification and CWB via job boredom. The model was tested using 3-wave data; however, since the data were attained from a single source, questions of common method bias cannot be ruled out. Managers should look for changes in employee attitudes and promptly modify employees' positions when they indicate that they have more experience, abilities, and talents required for their roles in their organizations.
Keywords: counterproductive work behavior; job boredom; job crafting; perceived overqualification; person–job (mis)fit.
Copyright © 2022 Khan, Ali, Saeed, Vega-Muñoz and Contreras-Barraza.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cross Culture Examination of Perceived Overqualification, Psychological Well-Being and Job Search: The Moderating Role of Proactive Behavior.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2024 Feb 14;17:553-566. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S441168. eCollection 2024. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2024. PMID: 38374936 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the nexus between perceived overqualification and knowledge hiding: Moderated mediation analysis of job crafting and job boredom.Heliyon. 2024 May 22;10(10):e31701. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31701. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38831809 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived overqualification as a double-edged sword for employee creativity: The mediating role of job crafting and work withdrawal behavior.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 17;19(6):e0304529. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304529. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38885235 Free PMC article.
-
Employee perceived overqualification and innovation performance: the roles of self-oriented perfectionism and job crafting.Front Psychol. 2024 Aug 7;15:1398163. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1398163. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39171221 Free PMC article.
-
Proactive Breakthrough or Passive Exhaustion? A Dual-Path Integrated Model Driven by Perceived Overqualification.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 May 19;15(5):702. doi: 10.3390/bs15050702. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40426479 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cross Culture Examination of Perceived Overqualification, Psychological Well-Being and Job Search: The Moderating Role of Proactive Behavior.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2024 Feb 14;17:553-566. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S441168. eCollection 2024. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2024. PMID: 38374936 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between person-environment fit and mental health - results from the population-based LIFE-Adult-Study.BMC Public Health. 2024 Aug 1;24(1):2083. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19599-z. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39090620 Free PMC article.
-
The impacts of achievement goal orientation, dark triad, person-environment misfit, and perceived psychological safety on external hires' deviant behaviors.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 8;15(1):24508. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09700-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40628924 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of abusive supervision on employee counterproductive work behavior: a moderated mediation analysis.Front Psychol. 2025 Jul 4;16:1455658. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1455658. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40688554 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Perceived Overqualification on Workplace Procrastination: The Role of Public Service Motivation and Perceived Prosocial Impact.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 Apr 28;15(5):590. doi: 10.3390/bs15050590. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40426368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiken L. S., West S. G., Reno R. R. (1991). Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions. New York, NY: Sage.
-
- Andel S., Pindek S., Arvan M. L. (2022). Bored, angry, and overqualified? The high-and low-intensity pathways linking perceived overqualification to behavioural outcomes. Eur. J. Work Organ. Psy. 31, 47–60. doi: 10.1080/1359432X.2021.1919624 - DOI
-
- Anderson J. C., Gerbing D. W. (1988). Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin 103:411.
-
- Arvan M. L., Pindek S., Andel S. A., Spector P. E. (2019). Too good for your job? Disentangling the relationships between objective overqualification, perceived overqualification, and job dissatisfaction. J. Vocat. Behav. 115:103323. doi: 10.1016/j.jvb.2019.103323 - DOI
-
- Bakker A. B., Tims M., Derks D. (2012). Proactive personality and job performance: the role of job crafting and work engagement. Hum. Relat. 65, 1359–1378. doi: 10.1177/0018726712453471 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources