Continuous Psychological Nursing Based on Grey Clustering Algorithm in Patients after Transurethral Resection of Prostate
- PMID: 35936363
- PMCID: PMC9352487
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5400479
Continuous Psychological Nursing Based on Grey Clustering Algorithm in Patients after Transurethral Resection of Prostate
Abstract
Objective: To explore the effect of continuous psychological nursing based on the grey clustering algorithm on erectile function, bad psychological emotion, and complications in patients after transurethral resection of prostate (TURP).
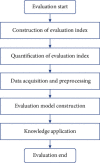
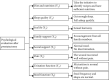
Methods: 98 patients who underwent TURP were randomly divided into observation and control groups (routine nursing). The observation group first used the grey clustering algorithm to evaluate the psychological intelligence, found patients with abnormal psychological behavior, and then implemented continuous psychological nursing combined with pelvic floor muscle exercise. The patients were followed up for 4 months. The International Index of Erectile Function-5 (IIEF-5), the incidence of complications, the Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD), the Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA) scores, and the nursing satisfaction were analyzed and compared between these two groups.
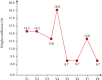
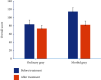
Results: The grey clustering algorithm can accurately reflect the characteristics of patients' psychological changes. After targeted nursing, compared with the control group, the IIEF-5 in the observation group was higher [(24.87 ± 1.85) vs. (22.24 ± 1.47), P < 0.05], the incidence of total complications was lower (10.20% vs. 26.53%, P < 0.05), the score of HAMA was lower [(6.11 ± 2.57) vs. (10.98 ± 2.29), P < 0.05], the score of HAMD was lower [(6.97 ± 2.85) vs. (11.35 ± 2.19), P < 0.05], and the nursing satisfaction was higher (100% vs. 85.71%, P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Mental intelligence evaluation based on the grey clustering algorithm combined with pelvic floor muscle exercise can significantly improve the rehabilitation effect of erectile function in patients after TURP, reduce the incidence of postoperative complications, and alleviate patients' anxiety and depression.
Copyright © 2022 Peiting Lu and Cuiyun Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of Hiraoka's Transurethral Detachment Prostatectomy and Transurethral Resection of the Prostate Effects on Postoperative Erectile Function in Patients With Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study.J Sex Med. 2020 Nov;17(11):2181-2190. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2020.06.001. Epub 2020 Jul 19. J Sex Med. 2020. PMID: 32665211 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of transurethral resection of the prostate on erectile function: a prospective comparative study.Int J Impot Res. 2010 Mar-Apr;22(2):146-51. doi: 10.1038/ijir.2009.56. Epub 2009 Nov 26. Int J Impot Res. 2010. PMID: 19940854
-
Efficacy and Safety Evaluation of Transurethral Resection of the Prostate versus Plasmakinetic Enucleation of the Prostate in the Treatment of Massive Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.Urol Int. 2021;105(9-10):735-742. doi: 10.1159/000511116. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Urol Int. 2021. PMID: 33524981
-
Comparison of photoselective green light laser vaporisation versus traditional transurethral resection for benign prostate hyperplasia: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials and prospective studies.BMJ Open. 2019 Aug 21;9(8):e028855. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028855. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31439603 Free PMC article.
-
Impact on Sexual Function of Endoscopic Enucleation vs Transurethral Resection of the Prostate for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Due to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Endourol. 2020 Oct;34(10):1064-1074. doi: 10.1089/end.2020.0141. Epub 2020 May 5. J Endourol. 2020. PMID: 32242462
Cited by
-
The incidence and influencing factors of hypothermia in patients after transurethral prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Urol. 2025 Jun 5;43(1):356. doi: 10.1007/s00345-025-05729-8. World J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40468122 Free PMC article.
-
Application effect of supportive psychological nursing combined with continuous nursing in patients with thyroid malignancy undergoing surgery.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21757. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07063-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596508 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of psychological nursing intervention on anxiety level and quality of life in patients with gastrointestinal peptic ulcer.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024 Sep 27;16(9):2953-2960. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i9.2953. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024. PMID: 39351561 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Application Effect of Postoperative Nursing Intervention on Patients Undergoing Transurethral Prostatectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2025 Feb;54(2):285-296. Iran J Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40225246 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wei H. B., Guo B. Y., Tu Y. F., et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of transurethral laser versus open prostatectomy for patients with large-sized benign prostatic hyperplasia: a meta-analysis of comparative trials. Investigative and Clinical Urology . 2022;63(3):262–272. doi: 10.4111/icu.20210281. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yuan Y., Hu Y., Cheng J. X., Ding P. Psychological nursing approach on anxiety and depression of patients with severe urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy - a pilot study. The Journal of International Medical Research . 2019;47(11):5689–5701. doi: 10.1177/0300060519878014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

