Synthesis of Novel Phthalazinedione-Based Derivatives with Promising Cytotoxic, Anti-bacterial, and Molecular Docking Studies as VEGFR2 Inhibitors
- PMID: 35936456
- PMCID: PMC9350887
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03182
Synthesis of Novel Phthalazinedione-Based Derivatives with Promising Cytotoxic, Anti-bacterial, and Molecular Docking Studies as VEGFR2 Inhibitors
Abstract
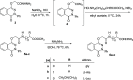
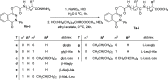
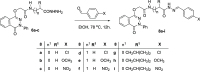
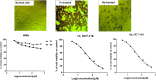
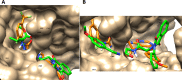
The parent ester methyl-3-[2-(4-oxo-3-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-phthalazin-1-yloxy)-acetylamino] has 18 compounds. The starting material for alkanoates, their corresponding hydrazides, hydrazones, and dipeptides were produced by chemoselective O-alkylation of 2-phenyl-2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione with ethyl chloroacetate(4-oxo-3-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-phthalazin-1-yloxy) acetic acid methyl ester. The starting ester was hydrazinolyzed, then azide coupled with amino acid ester hydrochloride to produce several parent esters, and then hydrazinolyzed to produce parent hydrazides. These hydrazides were used to make a series of dipeptides by reacting them with amino acid ester hydrochloride under azide coupling conditions, and they were also condensed with a number of aldehydes to make the hydrazones. These derivatives were subjected to cytotoxicity against HCT-116 and MDA-MB-231 cells and anti-bacterial and molecular docking studies. Results indicated that the tested compounds, especially 7c and 8b with the phenyl phthalazinone moieties, had promising cytotoxicity against the HCT-116 cells with IC50 values of 1.36 and 2.34 μM, respectively. Additionally, the promising compounds 7c and 8b exhibited poor cytotoxicity against WISH cells with much higher IC50 values, so they were safe against normal cells. Compound 8c exhibited potent anti-bacterial activity with inhibition zones of 12 and 11 mm against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, respectively. The molecular docking results of compounds 7c and 8b revealed a good binding disposition and the ligand-receptor interactions like the co-crystallized ligand of the VEGFR2 protein, which may be the proposed mode of action. Finally, compounds 7c and 8b exhibited good ADME pharmacokinetics with good drug-likeness parameters. Hence, detailed studies for the mechanism of action of such compounds are highly recommended for the development of new potent anti-cancer and anti-bacterial agents.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
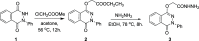
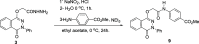
Similar articles
-
Synthesis of novel phthalazine-based derivatives with potent cytotoxicity against HCT-116 cells through apoptosis and VEGFR2 inhibition.RSC Adv. 2024 Apr 24;14(19):13027-13043. doi: 10.1039/d4ra02103g. eCollection 2024 Apr 22. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38660526 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of phthalazine-based derivatives as selective anti-breast cancer agents through EGFR-mediated apoptosis: in vitro and in silico studies.BMC Chem. 2023 Jul 27;17(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13065-023-00995-2. BMC Chem. 2023. PMID: 37501139 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, molecular docking, in silico ADMET profile and anticancer evaluations of sulfonamide endowed with hydrazone-coupled derivatives as VEGFR-2 inhibitors.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Mar;108:104669. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104669. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 33515863
-
Synthesis and Biological Activities of Some New Benzotriazinone Derivatives Based on Molecular Docking; Promising HepG2 Liver Carcinoma Inhibitors.ACS Omega. 2020 Mar 19;5(12):6781-6791. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00116. eCollection 2020 Mar 31. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32258913 Free PMC article.
-
Novel benzothiazole-based dual VEGFR-2/EGFR inhibitors targeting breast and liver cancers: Synthesis, cytotoxic activity, QSAR and molecular docking studies.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022 Feb 15;58:128529. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128529. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35007724 Review.
Cited by
-
Experimental and In Silico Evaluation of New Heteroaryl Benzothiazole Derivatives as Antimicrobial Agents.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Nov 18;11(11):1654. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111654. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421298 Free PMC article.
-
1-Benzyl-5-bromo-3-hydrazonoindolin-2-ones as Novel Anticancer Agents: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Modeling Insights.Molecules. 2023 Apr 4;28(7):3203. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073203. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049966 Free PMC article.
-
Novel curcumin-based analogues as potential VEGFR2 inhibitors with promising metallic loading nanoparticles: synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular modelling investigation.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Sep 27;15(12):4039-67. doi: 10.1039/d4md00574k. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39345715 Free PMC article.
-
Salicylaldehyde Benzoylhydrazone Protects Against Ferroptosis in Models of Neurotoxicity and Behavioural Dysfunction, In Vitro and In Vivo.J Mol Neurosci. 2025 Jun 14;75(2):77. doi: 10.1007/s12031-025-02371-2. J Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40515790 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of novel phthalazine-based derivatives with potent cytotoxicity against HCT-116 cells through apoptosis and VEGFR2 inhibition.RSC Adv. 2024 Apr 24;14(19):13027-13043. doi: 10.1039/d4ra02103g. eCollection 2024 Apr 22. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38660526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El Rayes S. M.; Aboelmagd A.; Gomaa M. S.; Ali I. A. I.; Fathalla W.; Pottoo F. H.; Khan F. A. Convenient Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of Methyl 2-[3-(3-Phenyl-Quinoxalin-2-Ylsulfanyl)Propanamido]Alkanoates and N-Alkyl 3-((3-Phenyl-Quinoxalin-2-Yl)Sulfanyl)Propanamides. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 18555–18566. 10.1021/acsomega.9b02320. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhai X.; Li J.; He L.; Zheng S.; Zhang Y. B.; Gong P. Synthesis and in Vitro Cytotoxicity of Novel 1,4-Disubstituted Phthalazines. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2008, 19, 29–32. 10.1016/j.cclet.2007.11.018. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

