Effect of Home Visits by Nurses on the Physical and Psychosocial Health of Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35936539
- PMCID: PMC9288399
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v51i4.9234
Effect of Home Visits by Nurses on the Physical and Psychosocial Health of Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: One of the best ways to maintain and develop physical and psychosocial health is to make regular home visits. This meta-analysis aimed to determine (by subgroups) the effects of interventions based on nurses' home visits on physical and psychological health outcomes of older people.
Methods: This search was carried out using the The CINAHL, Cochrane, MEDLINE, PubMed, Science Direct, Web of Science, and Turkish databases. Experimental and observational studies were included.
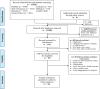
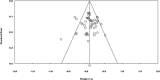
Results: The meta-analysis included 26 (with subgroups 50) out of 13110 studies. The minimum and maximum values of the effect size (Hedges g) were g = -0.708 and g = 0.525, respectively. The average effect size was g = 0.084 (SD = 0.21).
Conclusion: Home visit interventions are effective in reducing the frequency of hospitalization in the older adults, and improving physical and psychosocial health. They are negatively effective on falls and have no significant effect on the quality of life.
Keywords: Health; Home visit; Meta-analysis; Older adults; Systematic review.
Copyright © 2022 Ergin et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2019). World Population Ageing 2019: Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/430). https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/publications/pdf/agein.... Accessed 30 Sep 2019.
-
- Kruschke C. (2018). The role of the LPN as a leader and manager in the healthcare setting. In: Leadership skills for licensed practical nurses working with the aging population. Ed, Kruschke C. Springer, Cham, pp.47–59.
-
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2019). World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/423). https://population.un.org/wpp/Publications/Files/WPP2019_Highlights.pdf. Accessed 30 Sep 2019.
-
- Mathers CD, Stevens GA, Boerma T, et al. (2015). Causes of international increases in older age life expectancy. Lancet, 385 (9967):540–48. - PubMed
-
- Tezcan S, Seçkiner P. (2012). Demographic change in Turkey; age perspective. In: Elderly health: Issues and solutions. Dilek A, Melikşah E. (Eds.), Australia, Turkish Society of Public Health Specialists Press, pp.1–8.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources