Cross-Sectional Area Reference Values of Nerves in the Upper and Lower Extremities using Ultrasonography in the Indian Population
- PMID: 35936619
- PMCID: PMC9350782
- DOI: 10.4103/aian.aian_727_21
Cross-Sectional Area Reference Values of Nerves in the Upper and Lower Extremities using Ultrasonography in the Indian Population
Abstract
Background and purpose: Cross-sectional area (CSA) is the most important parameter to study peripheral nerves by high-resolution ultrasonography. The aim was to acquire normative data of CSA of the main upper and lower limb nerves in the Indian population.
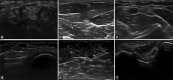
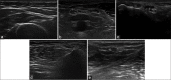
Methods: CSA of nerves was determined in 100 healthy volunteers at 11 predetermined sites: median and ulnar at the wrist, mid-forearm, elbow; radial (spiral groove); tibial (popliteal fossa, medial malleolus); common peroneal (CPN, fibular head) and sural (lateral malleolus).
Results: The mean age of participants was 40.7 ± 13.0 years (range: 18-79). Fifty were < 40 years of age. The mean height, weight and BMI were 161.5 ± 8.3 centimeters (range: 145-179), 58.6 ± 10.1 kilograms (range: 32-90) and 22.4 ± 3.2 kilogram/square meter (range: 14.03-30.44), respectively. The median and ulnar nerve measurements were non-uniform throughout its course, and the CSA was largest at the elbow and ulnar groove, respectively. With advancing age, there was a significant difference for median and ulnar nerves at the wrist (median P = 0.002, ulnar P = 0.009) and tibial nerve (popliteal fossa, P = 0.045, medial malleolus, P = 0.005), CPN (P = 0.047). Men had greater CSA of upper limb nerves and tibial nerves at popliteal fossa (P < 0.05) as compared to women. A positive correlation was noted with weight.
Conclusion: It is apt for every defined population to have its own set of normative data of CSA as it varies with ethnicity, age, and the built of individuals. We provide a valuable set of CSA data for nerves in the Indian population, which can be used for comparison while investigating peripheral nerve disorders.
Keywords: Cross-sectional area; India; normative data; peripheral nerve; ultrasound.
Copyright: © 2022 Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cross sectional area reference values for sonography of peripheral nerves and brachial plexus.Clin Neurophysiol. 2013 Sep;124(9):1881-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2013.03.007. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Clin Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 23583024
-
Cross-sectional area reference values for peripheral nerve ultrasound in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis-Part II: Lower extremity nerves.Eur J Neurol. 2021 Jul;28(7):2313-2318. doi: 10.1111/ene.14850. Epub 2021 May 7. Eur J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33794049
-
Cross-Sectional Area Reference Values for Sonography of Peripheral Nerves in Taiwanese Adults.Front Neurol. 2021 Nov 3;12:722403. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.722403. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34803870 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-sectional area reference values for high-resolution ultrasonography of the upper extremity nerves in healthy Asian adults.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 May 7;100(18):e25812. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025812. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33950986 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-sectional area reference values for peripheral nerve ultrasound in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis-Part I: Upper extremity nerves.Eur J Neurol. 2021 May;28(5):1684-1691. doi: 10.1111/ene.14759. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Eur J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33527596
Cited by
-
Normative Reference Values of the Tibial Nerve in Healthy Individuals Using Ultrasonography: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2023 Sep 25;12(19):6186. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196186. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37834829 Free PMC article.
-
Cut-off value for a normal posterior tibial nerve to diagnose tarsal tunnel syndrome amongst people of different race in Pretoria, South Africa.J Med Radiat Sci. 2024 Sep;71(3):396-402. doi: 10.1002/jmrs.792. Epub 2024 Apr 20. J Med Radiat Sci. 2024. PMID: 38641991 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Mutation in Frabin (FGD4) Causing a Mild Phenotype of CMT4H in an Indian Patient.J Neuromuscul Dis. 2024;11(1):221-232. doi: 10.3233/JND-230042. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2024. PMID: 38108359 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Sectional Area and Echogenicity Reference Values for Sonography of Peripheral Nerves in the Lithuanian Population.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 28;14(13):1373. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14131373. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001263 Free PMC article.
-
High-Resolution Ultrasound in Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients of Hansen's Disease.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2024 Dec 11;16(1):195. doi: 10.4103/idoj.idoj_464_24. eCollection 2025 Jan-Feb. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2024. PMID: 39850683 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Boehm J, Scheidl E, Bereczki D, Schelle T, Arányi Z. High-resolution ultrasonography of peripheral nerves: Measurements on 14 nerve segments in 56 healthy subjects and reliability assessments. Ultraschall Med. 2014;35:459–67. - PubMed
-
- Walker FO, Cartwright MS, Alter KE, Visser LH, Hobson-Webb LD, Padua L, et al. Indications for neuromuscular ultrasound: Expert opinion and review of the literature. Clin Neurophysiol. 2018;129:2658–79. - PubMed
-
- Burg EW, Bathala L, Visser LH. Difference in normal values of median nerve cross-sectional area between Dutch and Indian subjects. Muscle Nerve. 2014;50:129–32. - PubMed

