Emerging roles of platelets in cancer biology and their potential as therapeutic targets
- PMID: 35936717
- PMCID: PMC9355257
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.939089
Emerging roles of platelets in cancer biology and their potential as therapeutic targets
Abstract
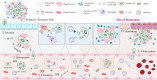
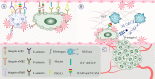
The main role of platelets is to control bleeding and repair vascular damage via thrombosis. They have also been implicated to promote tumor metastasis through platelet-tumor cell interactions. Platelet-tumor cell interactions promote tumor cell survival and dissemination in blood circulation. Tumor cells are known to induce platelet activation and alter platelet RNA profiles. Liquid biopsies based on tumor-educated platelet biomarkers can detect tumors and correlate with prognosis, personalized therapy, treatment monitoring, and recurrence prediction. Platelet-based strategies for cancer prevention and tumor-targeted therapy include developing drugs that target platelet receptors, interfere with the release of platelet particles, inhibit platelet-specific enzymes, and utilize platelet-derived "nano-platelets" as a targeted drug delivery platform for tumor therapy. This review elaborates on platelet-tumor cell interactions and the molecular mechanisms and discusses future research directions for platelet-based liquid biopsy techniques and platelet-targeted anti-tumor strategies.
Keywords: NETosis; immune escape; liquid biopsy; platelet activation; platelet aggregation activity; tumor metastasis; tumor treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Wang, Guo, Mao and Miao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

