A novel cuproptosis-related prognostic lncRNA signature and lncRNA MIR31HG/miR-193a-3p/TNFRSF21 regulatory axis in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35936736
- PMCID: PMC9353736
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.927706
A novel cuproptosis-related prognostic lncRNA signature and lncRNA MIR31HG/miR-193a-3p/TNFRSF21 regulatory axis in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
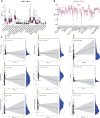
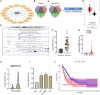
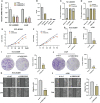
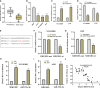
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) remains the most common subtype of lung malignancy. Cuproptosis is a newly identified cell death which could regulate tumor cell proliferation and progression. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are key molecules and potential biomarkers for diagnosing and treating various diseases. However, the effects of cuproptosis-related lncRNAs on LUAD are still unclear. In our study, 7 cuproptosis-related lncRNAs were selected to establish a prognostic model using univariate Cox regression analysis, LASSO algorithm, and multivariate analysis. Furthermore, we evaluated AC008764.2, AL022323.1, ELN-AS1, and LINC00578, which were identified as protective lncRNAs, while AL031667.3, AL606489.1, and MIR31HG were identified as risk lncRNAs. The risk score calculated by the prognostic model proved to be an effective independent factor compared with other clinical features by Cox regression analyses [univariate analysis: hazard ratio (HR) = 1.065, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.043-1.087, P < 0.001; multivariate analysis: HR = 1.067, 95% CI = 1.044-1.091, P < 0.001]. In addition, both analyses (ROC and nomogram) were used to corroborate the accuracy and reliability of this signature. The correlation between cuproptosis-related lncRNAs and immune microenvironment was elucidated, where 7 immune cells and 8 immune-correlated pathways were found to be differentially expressed between two risk groups. Furthermore, our results also identified and verified the ceRNA of cuproptosis-related lncRNA MIR31HG/miR-193a-3p/TNFRSF21 regulatory axis using bioinformatics tools. MIR31HG was highly expressed in LUAD specimens and some LUAD cell lines. Inhibition of MIR31HG clearly reduced the proliferation, migration, and invasion of the LUAD cells. MIR31HG showed oncogenic features via sponging miR-193a-3p and tended to positively regulate TNFRSF21 expression. In a word, lncRNA MIR31HG acts as an oncogene in LUAD by targeting miR-193a-3p to modulate TNFRSF21, which may be beneficial to the gene therapy of LUAD.
Keywords: MIR31HG; TNFRSF21; cuproptosis; lung adenocarcinoma; miR-193a-3p.
Copyright © 2022 Mo, Hu, Yang, Li, Bashir, Nai, Ma, Jia and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kuhn E, Morbini P, Cancellieri A, Damiani S, Cavazza A, Comin CE. Adenocarcinoma classification: Patterns and prognosis. Pathologica (2018) 110(1):5–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

