The Emerging Role of RNA N6-Methyladenosine Modification in Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 35936737
- PMCID: PMC9354683
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.927640
The Emerging Role of RNA N6-Methyladenosine Modification in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
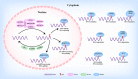
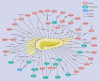
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is one of the most common malignant cancers, ranking the seventh highest causes of cancer-related deaths globally. Recently, RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is emerging as one of the most abundant RNA modifications in eukaryote cells, involved in multiple RNA processes including RNA translocation, alternative splicing, maturation, stability, and degradation. As reported, m6A was dynamically and reversibly regulated by its "writers", "erasers", and "readers", Increasing evidence has revealed the vital role of m6A modification in the development of multiple types of cancers including PC. Currently, aberrant m6A modification level has been found in both PC tissues and cell lines. Moreover, abnormal expressions of m6A regulators and m6A-modified genes have been reported to contribute to the malignant development of PC. Here in this review, we will focus on the function and molecular mechanism of m6A-modulated RNAs including coding RNAs as well as non-coding RNAs. Then the m6A regulators will be summarized to reveal their potential applications in the clinical diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutics of PC.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine (m6A); RNA methylation; coding RNAs; non-coding RNAs; pancreatic cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Hu, Lei, Guo, Fu, Sun, Lu, Su, Xu and Tu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Javadrashid D, Baghbanzadeh A, Derakhshani A, Leone P, Silvestris N, Racanelli V, et al. Pancreatic Cancer Signaling Pathways, Genetic Alterations, and Tumor Microenvironment: The Barriers Affecting the Method of Treatment. Biomedicines (2021) 9(4):373. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9040373 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials