Tumor microbiome metabolism: A game changer in cancer development and therapy
- PMID: 35936744
- PMCID: PMC9351545
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.933407
Tumor microbiome metabolism: A game changer in cancer development and therapy
Abstract
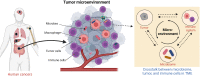
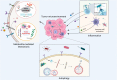
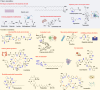
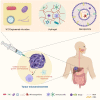
Accumulating recent evidence indicates that the human microbiome plays essential roles in pathophysiological states, including cancer. The tumor microbiome, an emerging concept that has not yet been clearly defined, has been proven to influence both cancer development and therapy through complex mechanisms. Small molecule metabolites produced by the tumor microbiome through unique biosynthetic pathways can easily diffuse into tissues and penetrate cell membranes through transporters or free diffusion, thus remodeling the signaling pathways of cancer and immune cells by interacting with biomacromolecules. Targeting tumor microbiome metabolism could offer a novel perspective for not only understanding cancer progression but also developing new strategies for the treatment of multiple cancer types. Here, we summarize recent advances regarding the role the tumor microbiome plays as a game changer in cancer biology. Specifically, the metabolites produced by the tumor microbiome and their potential effects on the cancer development therapy are discussed to understand the importance of the microbial metabolism in the tumor microenvironment. Finally, new anticancer therapeutic strategies that target tumor microbiome metabolism are reviewed and proposed to provide new insights in clinical applications.
Keywords: cancer development; cancer therapy; immune response; metabolism; tumor microbiome.
Copyright © 2022 Zhou, Kandalai, Hossain and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

