Deep-LC: A Novel Deep Learning Method of Identifying Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer-Related Genes
- PMID: 35936745
- PMCID: PMC9353732
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.949546
Deep-LC: A Novel Deep Learning Method of Identifying Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer-Related Genes
Abstract
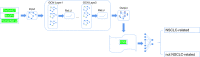
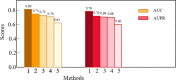
According to statistics, lung cancer kills 1.8 million people each year and is the main cause of cancer mortality worldwide. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for over 85% of all lung cancers. Lung cancer has a strong genetic predisposition, demonstrating that the susceptibility and survival of lung cancer are related to specific genes. Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) and next-generation sequencing have been used to discover genes related to NSCLC. However, many studies ignored the intricate interaction information between gene pairs. In the paper, we proposed a novel deep learning method named Deep-LC for predicting NSCLC-related genes. First, we built a gene interaction network and used graph convolutional networks (GCNs) to extract features of genes and interactions between gene pairs. Then a simple convolutional neural network (CNN) module is used as the decoder to decide whether the gene is related to the disease. Deep-LC is an end-to-end method, and from the evaluation results, we can conclude that Deep-LC performs well in mining potential NSCLC-related genes and performs better than existing state-of-the-art methods.
Keywords: Deep-LC; convolutional neural network (CNN) accelerator; genome-wide association analysis; graph convolutional networks; non-small cell lung cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Meng, Liu, Ma, Sun and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Navada S, Lai P, Schwartz AG, Kalemkerian GP. Temporal Trends in Small Cell Lung Cancer: Analysis of the National Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End-Results (SEER) Database. J Clin Oncol (2006) 24(18_suppl):7082–2. doi: 10.1200/jco.2006.24.18_suppl.7082 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources