Diagnostic value of striatal 18F-FP-DTBZ PET in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 35936768
- PMCID: PMC9355024
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.931015
Diagnostic value of striatal 18F-FP-DTBZ PET in Parkinson's disease
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Diagnostic value of striatal 18F-FP-DTBZ PET in Parkinson's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Sep 14;14:1029024. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1029024. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36185482 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: 18F-FP-DTBZ has been proven as a biomarker for quantifying the concentration of presynaptic vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2). However, its clinical application is still limited.
Objectives: To evaluate the difference in dopaminergic integrity between patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) and healthy controls (HC) using 18F-FP-DTBZ PET in vivo and to determine the diagnostic value of standardized uptake value ratios (SUVRs) using the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve.
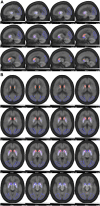
Methods: A total of 34 PD and 31 HC participants were enrolled in the PET/MR derivation cohort, while 89 PD and 18 HC participants were recruited in the PET/CT validation cohort. The Hoehn-Yahr Scale and the third part of the MDS-Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (MDSUPDRS-III) were used to evaluate the disease staging and severity. All assessments and PET scanning were performed in drug-off states. The striatum was segmented into five subregions as follows: caudate, anterior dorsal putamen (ADP), anterior ventral putamen (AVP), posterior dorsal putamen (PDP), and posterior ventral putamen (PVP) using automatic pipeline built with the PMOD software (version 4.105). The SUVRs of the targeted subregions were calculated using the bilateral occipital cortex as the reference region.
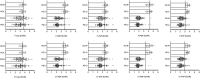
Results: Regarding the diagnostic value, ROC curve and blind validation showed that the contralateral PDP (SUVR = 3.43) had the best diagnostic accuracy (AUC = 0.973; P < 0.05), with a sensitivity of 97.1% (95% CI: 82.9-99.8%), specificity of 100% (95% CI: 86.3-100%), positive predictive value (PPV) of 100% (95% CI: 87.0-100%), negative predictive value (NPV) of 96.9% (95% CI: 82.0-99.8%), and an accuracy of 98.5% for the diagnosis of PD in the derivation cohort. Blind validation of 18F-FP-DTBZ PET imaging diagnosis was done using the PET/CT cohort, where participants with a SUVR of the PDP <3.43 were defined as PD. Kappa test showed a consistency of 0.933 (P < 0.05) between clinical diagnosis and imaging diagnosis, with a sensitivity of 98.9% (95% CI: 93.0-99.9%), specificity of 94.4% (95% CI: 70.6-99.7%), PPV of 98.9% (95% CI: 93.0-99.9%), NPV of 94.4% (95% CI: 70.6-99.7%), and a diagnostic accuracy of 98.1%.
Conclusions: Our results showed that an SUVR threshold of 3.43 in the PDP could effectively distinguish patients with PD from HC.
Keywords: 18F-FP-DTBZ; Parkinson’s disease; VMAT2; diagnostic value; positron emission tomography.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Liu, Barret, Tamagnan, Qiao, Song, Lu and Chan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander P. K., Lie Y., Jones G., Sivaratnam C., Bozinvski S., Mulligan R. S., et al. (2017). Management impact of imaging brain vesicular monoamine transporter type 2 in clinically uncertain Parkinsonian syndrome with 18F-AV133 and PET. J. Nucl. Med. 58 1815–1820. 10.2967/jnumed.116.189019 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benamer H. T., Oertel W. H., Patterson J., Hadley D. M., Pogarell O., Höffken H., et al. (2003). Prospective study of presynaptic dopaminergic imaging in patients with mild parkinsonism and tremor disorders: part 1. Baseline and 3-month observations. Mov. Disord. 18 977–984. 10.1002/mds.10482 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

