Advances in UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine Enolpyruvyl Transferase (MurA) Covalent Inhibition
- PMID: 35936791
- PMCID: PMC9346081
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.889825
Advances in UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine Enolpyruvyl Transferase (MurA) Covalent Inhibition
Abstract
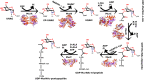
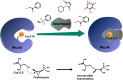
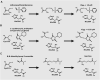
Peptidoglycan is a cross-linked polymer responsible for maintaining the bacterial cell wall integrity and morphology in Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. The peptidoglycan pathway consists of the enzymatic reactions held in three steps: cytoplasmic, membrane-associated, and periplasmic. The Mur enzymes (MurA-MurF) are involved in a cytoplasmic stage. The UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase (MurA) enzyme is responsible for transferring the enolpyruvate group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UNAG) to form UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvate (EP-UNAG). Fosfomycin is a natural product analogous to PEP that acts on the MurA target enzyme via binding covalently to the key cysteine residue in the active site. Similar to fosfomycin, other MurA covalent inhibitors have been described with a warhead in their structure that forms a covalent bond with the molecular target. In MurA, the nucleophilic thiolate of Cys115 is pointed as the main group involved in the warhead binding. Thus, in this minireview, we briefly describe the main recent advances in the design of MurA covalent inhibitors.
Keywords: MurA enzyme; bacterial resistance; covalent inhibitors; fosfomycin; peptidoglycan.
Copyright © 2022 de Oliveira, Furtado, da Costa, Vakal and Lima.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

