Facial myonecrosis following COVID-19
- PMID: 35936875
- PMCID: PMC9340454
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.07.030
Facial myonecrosis following COVID-19
Abstract
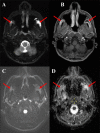
Myositis and myonecrosis are rare sequela of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Until now, it has not been seen in muscles of the head and neck. We present a 22-year-old male with 4 months of retroauricular headaches following COVID-19 infection. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed rim-enhancing fluid collections in the bilateral masticator spaces which were sampled by fine-needle aspiration. We also discuss this case in the context of the current understanding of COVID-19-related myositis.
Keywords: ADC, apparent diffusion coefficient; COVID-19; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; CT, computed tomography; DWI, diffusion-weighted imaging; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; Myonecrosis; Myositis.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

