Effects of Dietary Bopu Powder Supplementation on Serum Antioxidant Capacity, Egg Quality, and Intestinal Microbiota of Laying Hens
- PMID: 35936887
- PMCID: PMC9353574
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.902784
Effects of Dietary Bopu Powder Supplementation on Serum Antioxidant Capacity, Egg Quality, and Intestinal Microbiota of Laying Hens
Abstract
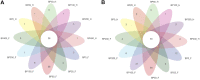
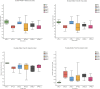
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of dietary Bopu powder supplementation on the serum antioxidant capacity, serum biochemical indices, egg quality, and intestinal microbiota. Six hundred and forty-eight 33-week-old Lohmann Brown commercial laying hens were randomly allocated into six groups and fed a basal diet supplemented with 0, 25, 50, 100, 200, and 400 mg/kg Bopu powder for 8 weeks, denoted BP0, BP25, BP50, BP100, BP200, and BP400, respectively. The results showed that dietary Bopu powder supplementation reduced serum cholesterol concentrations (linear, p < 0.01) while increasing serum globulin and albumin concentrations (linear, p < 0.05). Furthermore, the BP50 and BP100 groups had greater serum catalase and glutathione peroxidase activity (p < 0.05). The egg Haugh Units were considerably higher in BP25 and BP50 (p < 0.05), and eggshell thickness was higher in BP25, BP200, and BP400 (p < 0.05) when compared to BP0. Dietary treatment with Bopu powder at doses ranging from 25-100 mg/kg improved glutathione peroxidase and catalase activities while decreasing malondialdehyde concentrations in the yolk (p < 0.05). The addition of Bopu powder increased the diversity of microbiota and the relative abundance of Bacteroidota in the gut. For instance, dietary Bopu powder supplementation of 25-50 mg/kg significantly raised the relative abundance of Enterococcus, Bacteroides, and Fusobacterium in the foregut. Supplementing the diet with 50-100 mg/kg of Bopu powder improved the relative abundance of Lactobacillus in the hindgut. In conclusion, dietary Bopu powder supplementation enhanced the abundance of beneficial bacteria in the foregut of laying hens and improved egg quality and antioxidant capacity. Furthermore, in the laying hen diet, the optimal dosage of Bopu powder additive was 25-50 mg/kg.
Keywords: Bopu powder; antioxidant capacity; egg quality; gut microbiota; laying hens.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Lin, Liu, Huang, Yang, Cao, Liu, Li, Zeng and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Effects of dietary Bopu powder supplementation on intestinal development and microbiota in broiler chickens.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 13;13:1019130. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1019130. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36312926 Free PMC article.
-
Peppermint extract improves egg production and quality, increases antioxidant capacity, and alters cecal microbiota in late-phase laying hens.Front Microbiol. 2023 Sep 21;14:1252785. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1252785. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37808324 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dietary Inclusion of Dry Hydrastis canadensis on Laying Performance, Egg Quality, Serum Biochemical Parameters and Cecal Microbiota in Laying Hens.Animals (Basel). 2021 May 13;11(5):1381. doi: 10.3390/ani11051381. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067964 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Phytosterol Ester Supplementation on Egg Characteristics, Eggshell Ultrastructure, Antioxidant Capacity, Liver Function and Hepatic Metabolites of Laying Hens during Peak Laying Period.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 12;13(4):458. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040458. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671906 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dietary supplementation of organic zinc on laying performance, egg quality and some biochemical parameters of laying hens.J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2018 Apr;102(2):e542-e549. doi: 10.1111/jpn.12793. Epub 2017 Oct 9. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2018. PMID: 28990706 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Age-driven changes in the layer hen reproductive microbiome are associated with lay performance.Poult Sci. 2025 Aug 18;104(11):105703. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105703. Online ahead of print. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40850119 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of Macleaya cordata isoquinoline alkaloids on lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in broilers.Anim Biosci. 2024 Jan;37(1):131-141. doi: 10.5713/ab.23.0267. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Anim Biosci. 2024. PMID: 37946426 Free PMC article.
-
Macleaya cordata isoquinoline alkaloids attenuate Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal epithelium injury in broiler chickens by co-regulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 17;14:1335359. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1335359. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38299145 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary Bopu powder supplementation on intestinal development and microbiota in broiler chickens.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 13;13:1019130. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1019130. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36312926 Free PMC article.
-
Acute, chronic, and genotoxic studies on the protopine total alkaloids of the Macleaya cordata (willd.) R. Br. in rodents.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 28;13:987800. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.987800. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36249819 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

