3D Cell Cultures: Evolution of an Ancient Tool for New Applications
- PMID: 35936888
- PMCID: PMC9353320
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.836480
3D Cell Cultures: Evolution of an Ancient Tool for New Applications
Abstract
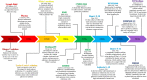
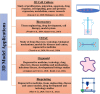
Recently, research is undergoing a drastic change in the application of the animal model as a unique investigation strategy, considering an alternative approach for the development of science for the future. Although conventional monolayer cell cultures represent an established and widely used in vitro method, the lack of tissue architecture and the complexity of such a model fails to inform true biological processes in vivo. Recent advances in cell culture techniques have revolutionized in vitro culture tools for biomedical research by creating powerful three-dimensional (3D) models to recapitulate cell heterogeneity, structure and functions of primary tissues. These models also bridge the gap between traditional two-dimensional (2D) single-layer cultures and animal models. 3D culture systems allow researchers to recreate human organs and diseases in one dish and thus holds great promise for many applications such as regenerative medicine, drug discovery, precision medicine, and cancer research, and gene expression studies. Bioengineering has made an important contribution in the context of 3D systems using scaffolds that help mimic the microenvironments in which cells naturally reside, supporting the mechanical, physical and biochemical requirements for cellular growth and function. We therefore speak of models based on organoids, bioreactors, organ-on-a-chip up to bioprinting and each of these systems provides its own advantages and applications. All of these techniques prove to be excellent candidates for the development of alternative methods for animal testing, as well as revolutionizing cell culture technology. 3D systems will therefore be able to provide new ideas for the study of cellular interactions both in basic and more specialized research, in compliance with the 3R principle. In this review, we provide a comparison of 2D cell culture with 3D cell culture, provide details of some of the different 3D culture techniques currently available by discussing their strengths as well as their potential applications.
Keywords: 3D cell culture; bioreactors; in vitro; organ-on-a-chip; organoids.
Copyright © 2022 Cacciamali, Villa and Dotti.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A brief history of organoids.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Jul 1;319(1):C151-C165. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00120.2020. Epub 2020 May 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32459504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spheroid-Hydrogel-Integrated Biomimetic System: A New Frontier in Advanced Three-Dimensional Cell Culture Technology.Cells Tissues Organs. 2025;214(2):128-147. doi: 10.1159/000541416. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Cells Tissues Organs. 2025. PMID: 39265553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic scaffolds for 3D cell cultures and organoids: applications in regenerative medicine.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2022 May;42(3):468-486. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2021.1932716. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34187261 Review.
-
Gaining New Biological and Therapeutic Applications into the Liver with 3D In Vitro Liver Models.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020 Dec;17(6):731-745. doi: 10.1007/s13770-020-00245-9. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020. PMID: 32207030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D Bioprinting and Its Application to Military Medicine.Mil Med. 2020 Sep 18;185(9-10):e1510-e1519. doi: 10.1093/milmed/usaa121. Mil Med. 2020. PMID: 32514549
Cited by
-
Toward Fully Automated Personalized Orthopedic Treatments: Innovations and Interdisciplinary Gaps.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Aug 12;11(8):817. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11080817. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cortical neurosphere model to study pathomechanisms and chemical toxicity in Kleefstra syndrome.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 29;14(1):22572. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72791-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39343771 Free PMC article.
-
A multimodal in vitro approach to assess the safety of oral care products using 2D and 3D cellular models.Front Toxicol. 2024 Nov 6;6:1474583. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2024.1474583. eCollection 2024. Front Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39568718 Free PMC article.
-
Growing Role of 3D In Vitro Cell Cultures in the Study of Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms: Short Focus on Breast Cancer, Endometriosis, Liver and Infectious Diseases.Cells. 2024 Jun 18;13(12):1054. doi: 10.3390/cells13121054. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38920683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteochondral organoids: current advances, applications, and upcoming challenges.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Jun 21;15(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03790-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38902814 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous