Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Brain Function and Emergence Agitation of Patients with Dexmedetomidine-Assisted General Anesthesia under Comfortable Nursing Intervention
- PMID: 35936982
- PMCID: PMC9347218
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8527568
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Brain Function and Emergence Agitation of Patients with Dexmedetomidine-Assisted General Anesthesia under Comfortable Nursing Intervention
Abstract
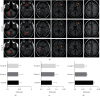
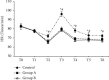
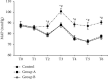
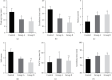
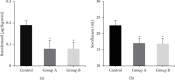
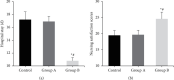
In order to explore the effects of dexmedetomidine (DEX) on functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and emergence agitation of patients who underwent general anesthesia surgery with sevoflurane under comfortable nursing intervention, 66 patients who received upper abdominal surgery were selected as research objects. According to nursing and anesthesia methods, the patients were randomly divided into control group (routine nursing and anesthesia), group A (routine nursing and DEX-assisted anesthesia), and group B (comfortable nursing and DEX-assisted anesthesia). The differences in the brain fMRI characteristics, hemodynamic indexes, anesthesia recovery indexes, and nursing satisfaction in the perioperative period were evaluated. The results showed that the regional homogeneity values were different in different brain regions, but there was no difference in the Z value of functional connectivity(P > 0.05). Compared with the control group, heart rate, mean arterial pressure, awakening time, extubation time, the Riker sedation-agitation scale (SAS) score, and anesthetic dosage were signally decreased in group A and group B, while the Ramsay scores, the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) stay, and anesthesia maintenance time in the two groups was obviously increased(P < 0.05). Compared with group A, the extubation time, the SAS score, PACU stay, and hospital stay were all remarkably reduced in group B, while the nursing satisfaction score was greatly increased(P < 0.05). To sum up, DEX was helpful to safely and effectively reduce the occurrence of emergence agitation in patients under general anesthesia surgery with sevoflurane. Besides, comfortable nursing intervention could further reduce the incidence of emergence agitation in patients with general anesthesia, shorten the length of hospital stay, and improve nursing satisfaction.
Copyright © 2022 Jingnan Gao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

