The diagnostic utility of IL-10, IL-17, and PCT in patients with sepsis infection
- PMID: 35937269
- PMCID: PMC9355284
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.923457
The diagnostic utility of IL-10, IL-17, and PCT in patients with sepsis infection
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study is to determine the diagnostic value and net clinical benefit of interleukin-10 (IL-10), interleukin-17 (IL-17), procalcitonin (PCT), and combination tests in patients with sepsis, which will serve as a standard for sepsis early detection.
Patients and methods: An investigation of 84 sepsis patients and 81 patients with local inflammatory diseases admitted to the ICU of Tongji University Hospital in 2021. In addition to comparing inter-group variability, indicators relevant to sepsis diagnosis and therapy were screened.
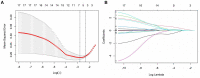
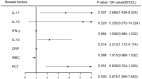
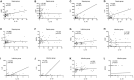
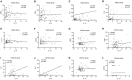
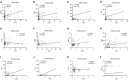
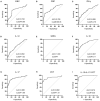
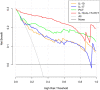
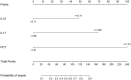
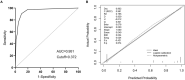
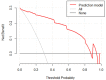
Results: LASSO regression was used to examine PCT, WBC, CRP, IL-10, IFN-, IL-12, and IL-17. Multivariate logistic regression linked IL-10, IL-17, and PCT to sepsis risk. The AUC values of IL-10, IL-17, PCT, and the combination of the three tests were much higher than those of standard laboratory infection indicators. The combined AUC was greater than the sum of IL-10, IL-17, and PCT (P < 0.05). A clinical decision curve analysis of IL-10, IL-17, PCT, and the three combined tests found that the three combined tests outperformed the individual tests in terms of total clinical benefit rate. To predict the risk of sepsis using IL-10, IL-17, and PCT had an AUC of 0.951, and the model's predicted probability was well matched. An examination of the nomogram model's clinical value demonstrated a considerable net therapeutic benefit between 3 and 87%.
Conclusion: The IL-10, IL-17, and PCT tests all have a high diagnostic value for patients with sepsis, and the combination of the three tests outperforms the individual tests in terms of diagnostic performance, while the combined tests have a higher overall clinical benefit rate.
Keywords: IL-10; IL-17; PCT; diagnostic value; nomogram; sepsis.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Wang, Hou, Jiang, Hu, Sun, Hu, Wu and Shang.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Diagnostic value of a combination of biomarkers in patients with sepsis and severe sepsis in emergency department].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014 Mar;26(3):153-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.03.006. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014. PMID: 24598287 Chinese.
-
[Diagnostic values of procalcitonin, interleukin-6, C reactive protein and serum amyloid A in sepsis].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2012 Sep;43(5):702-5. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2012. PMID: 23230743 Chinese.
-
[Value of Hepcidin as a diagnostic biomarker of sepsis in critically ill adults].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Jul;30(7):652-657. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.07.007. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 30045792 Chinese.
-
The efficacy of procalcitonin as a biomarker in the management of sepsis: slaying dragons or tilting at windmills?Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2013 Dec;14(6):489-511. doi: 10.1089/sur.2012.028. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2013. PMID: 24274059 Review.
-
Usefulness of estimation of blood procalcitonin concentration versus C-reactive protein concentration and white blood cell count for therapeutic monitoring of sepsis in neonates.Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014 Dec 21;68:1516-23. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1133101. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014. PMID: 25531715 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of interleukins in the detection of neonatal sepsis: a network meta-analysis.Front Pediatr. 2023 Nov 2;11:1267777. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1267777. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 38027268 Free PMC article.
-
The Value of Serum Procalcitonin, Thromboelastography Combined with Platelet Count in Predicting the Short-Term Progression of Septic Shock in the Intensive Care Unit.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Jul 31;17:3361-3370. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S464566. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39100724 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleated red blood cells as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis and prediction of sepsis severity in children.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Nov 1;13:1264607. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1264607. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38029254 Free PMC article.
-
Sepsis risk in diabetic patients with urinary tract infection.PLoS One. 2024 May 21;19(5):e0303557. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303557. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38771840 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and Risk Factors for Pediatric Sepsis.Curr Med Sci. 2024 Jun;44(3):648-656. doi: 10.1007/s11596-024-2870-6. Epub 2024 May 15. Curr Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38748371
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

