Experiences and needs of front-line nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and qualitative meta-synthesis
- PMID: 35937273
- PMCID: PMC9354751
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.805631
Experiences and needs of front-line nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and qualitative meta-synthesis
Abstract
Background: Front-line nurses have played a critical role during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. A number of qualitative studies reported front-line nurses' experiences and needs in caring for patients with COVID-19. However, the application of evidence from a single qualitative study to guide clinical practice has limitations. This study aimed to explore front-line nurses' experiences and needs during the COVID-19 pandemic through a qualitative meta-synthesis.
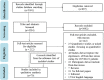
Methods: Seven databases were searched from 1 December 2019 to 20 January 2022, including PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane COVID-19 study register, CINAHL, PsycINFO, MedRxiv, and bioRxiv. The quality of included studies was appraised using the Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP) qualitative research appraisal tool. Meta-synthesis was used to synthesize the data from included studies.
Results: A total of 70 studies were included, and five synthesized findings were developed: (1) Although nurses actively devoted themselves to fighting against COVID-19, considering their professional responsibility and historical previous experience with mankind, they were not invulnerable; (2) There were various difficulties and challenges in caring for patients with COVID-19, including fear related to providing patients with care, shortage of protective equipment and manpower, and negative attitude of family members; (3) Facing difficulties and challenges, nurses could only partly cope by using mixed means to overcome those, including media, learning, gaining skills, responding together, and organizational assistance; (4) To better respond to the COVID-19 pandemic, nurses' needs should be paid attention to. Counseling, training, information, resources, and investment are pivotal; (5) Despite the hardships, nurses became stronger and gained gratitude, positivity, mental peace, and confidence.
Conclusions: This study reveals that the psychological experiences of front-line nurses varied, and they faced a variety of challenges. Although nurses had some coping strategies, they still needed multifaceted support to meet the challenges.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, PROSPERO: CRD42021255468.
Keywords: coronavirus disease 2019; experiences; needs; nurses; qualitative meta-synthesis; systematic review.
Copyright © 2022 Ding, Deng, Zhang, Wang, Liu, Huang and Yang.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experiences of intensive care unit nurses working with COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-synthesis of qualitative studies.Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 15;10:1034624. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1034624. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36466502 Free PMC article.
-
Nurses' caring experiences in COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review of qualitative research.Health Sci Rev (Oxf). 2022 Jun;3:100030. doi: 10.1016/j.hsr.2022.100030. Epub 2022 May 21. Health Sci Rev (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35615410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lessons from past epidemics and pandemics and a way forward for pregnant women, midwives and nurses during COVID-19 and beyond: A meta-synthesis.Midwifery. 2020 Nov;90:102821. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2020.102821. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Midwifery. 2020. PMID: 32847770 Free PMC article.
-
Experience of clinical nurses engaged in caring for patients with COVID-19: A qualitative systematic review and meta-synthesis.J Clin Nurs. 2023 Aug;32(15-16):5258-5273. doi: 10.1111/jocn.16613. Epub 2023 Jan 14. J Clin Nurs. 2023. PMID: 36639947
-
Nurses' barriers to caring for patients with COVID-19: a qualitative systematic review.Int Nurs Rev. 2021 Jun;68(2):202-213. doi: 10.1111/inr.12648. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Int Nurs Rev. 2021. PMID: 33420749 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Negative impact of nurses' fear of COVID-19: the moderating role of implementation of knowledge management.Front Public Health. 2024 Jul 25;12:1426408. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1426408. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39118971 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological Well-Being of Nurses with One to Five Years of Clinical Experience.SAGE Open Nurs. 2024 May 21;10:23779608241255300. doi: 10.1177/23779608241255300. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. SAGE Open Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38779615 Free PMC article.
-
Influential factors affecting nursing performance amid COVID-19: A cross-sectional study on nurse preparedness for infectious diseases.Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2024 Sep 6;7:100239. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnsa.2024.100239. eCollection 2024 Dec. Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2024. PMID: 39391566 Free PMC article.
-
Nurse-Patient Communication and Relationship When Wearing Personal Protective Equipment: Nurses' Experience in a COVID-19 Ward.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jul 7;11(13):1960. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11131960. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444794 Free PMC article.
-
Framing the Multi-Centre Qualitative Research Design as a Novel Methodology for Nursing and Healthcare Research: Reflections and A Methodological Discussion.J Adv Nurs. 2025 Aug;81(8):5196-5207. doi: 10.1111/jan.16548. Epub 2024 Oct 24. J Adv Nurs. 2025. PMID: 39445699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General's Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19-11 March 2020 (2020). Available from: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/whodirector-general-s-opening-rem... (accessed March 18, 2020).
-
- World Health Organization. Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19 - 8 March 2022 (2022). Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on... (accessed March 8, 2022).
-
- People's Network,. National Health Health Commission: 68% of Nurses Supporting the Frontline Medical Staff (2020). Available from: http://health.people.com.cn/n1/2020/0229/c14739-31610814.html (accessed March 18, 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical