Clinical Effect of Microneedle Injection Combined with Blood Transfusion in the Treatment of Severe Anemia Complicated with Vitiligo under Regenerative Medical Technology
- PMID: 35937386
- PMCID: PMC9355759
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7117627
Clinical Effect of Microneedle Injection Combined with Blood Transfusion in the Treatment of Severe Anemia Complicated with Vitiligo under Regenerative Medical Technology
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Clinical Effect of Microneedle Injection Combined with Blood Transfusion in the Treatment of Severe Anemia Complicated with Vitiligo under Regenerative Medical Technology.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9854137. doi: 10.1155/2024/9854137. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38230174 Free PMC article.
Abstract
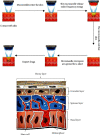
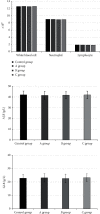
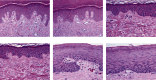
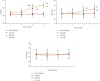
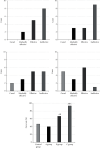
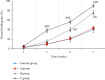
To explore the clinical efficacy of microneedle injection combined with blood transfusion in the treatment of severe anemia complicated with vitiligo based on regenerative medical technology and provide the theoretical basis for the adoption of microneedle technology, 60 patients with severe anemia complicated with vitiligo were selected as research objects. With 15 patients in each group, they were randomly assigned to the control group (calcipotriol ointment external application), observation group A (external application of moist exposed burn ointment (MEBO), observation group B (external application of MEBO combined with blood transfusion), and observation group C (microneedle injection of MEBO combined with blood transfusion). Blood indexes and plaque recovery of patients in different periods were detected. The total protein (TP) content in group C (62.3 ± 3.3 g/L and 64.3 ± 2.88 g/L) was remarkably higher than that in the control group (51.3 ± 3.17 g/L and 52.4 ± 3.17 g/L) and group A (52.6 ± 2.91 g/L and 51.8 ± 2.98 g/L)) at the 5th and 7th weeks after the treatment (P < 0.05). The albumin (ALB) content in group C (42.9 ± 3.28 g/L and 45.3 ± 3.1 g/L) was signally higher than that in the control group (41.8 ± 3.44 g/L and 41.9 ± 3.23 g/L) and group A (41.3 ± 2.91 g/L and 42.1 ± 3.02 g/L) at the 5th and 7th weeks after the treatment, and the content was markedly higher than that in group B at 5th week (P < 0.05). The wound healing rates of group C at the 3rd, 5th, and 7th weeks after the treatment (38.44%, 56.6%, and 90.23%) were greatly higher than those of the control group, group A, and group B (P < 0.05). Besides, the wound healing rate of group B was higher than that of the control group and group A (40.3% and 75.8%) at the 5th and 7th weeks after the treatment (P < 0.05). To sum up, based on regenerative medical technology, microneedle injection (microneedling is a derma roller process that pricks the skin with minuscule needles. The goal of the treatment is to develop new collagen and skin tissue, resulting in skin that is smoother, firmer, and more toned) combined with blood transfusion had a good therapeutic effect on patients with severe anemia complicated with vitiligo, which could manifestly improve the blood indexes and skin plaques of patients, with a good clinical adoption effect.
Copyright © 2022 Tao He and Li Gong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Retracted: Clinical Effect of Microneedle Injection Combined with Blood Transfusion in the Treatment of Severe Anemia Complicated with Vitiligo under Regenerative Medical Technology.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9854137. doi: 10.1155/2024/9854137. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38230174 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the efficacy of transdermal drug delivery of calcipotriol plus betamethasone versus tacrolimus in the treatment of vitiligo.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019 Apr;18(2):581-588. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12704. Epub 2018 Jul 16. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30009490 Clinical Trial.
-
Combined application of moist exposed burn ointment and maggot therapy in wound healing.J Wound Care. 2022 Oct 1;31(Sup10):S41-S52. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2022.31.Sup10.S41. J Wound Care. 2022. PMID: 36240870
-
Microneedling in vitiligo: A systematic review.Dermatol Ther. 2020 Nov;33(6):e14297. doi: 10.1111/dth.14297. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Dermatol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32940387
-
The use of moist exposed burn ointment (MEBO) for the treatment of burn wounds: a systematic review.J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2020 Dec;54(6):337-343. doi: 10.1080/2000656X.2020.1813148. Epub 2020 Sep 2. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2020. PMID: 32876517
Cited by
-
Retracted: Clinical Effect of Microneedle Injection Combined with Blood Transfusion in the Treatment of Severe Anemia Complicated with Vitiligo under Regenerative Medical Technology.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9854137. doi: 10.1155/2024/9854137. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38230174 Free PMC article.
-
Microneedle-Based Approaches for Skin Disease Treatment.Nanomicro Lett. 2025 Feb 6;17(1):132. doi: 10.1007/s40820-025-01662-y. Nanomicro Lett. 2025. PMID: 39909997 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lorentzen K., Kjær B., Olsen K. S. Treatment of severe anaemia in patients who refuse blood transfusion. Ugeskrift for Laeger . 2014;176(7) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

