A macroscopic anatomical study of the appropriate palpation zone of the gluteus medius muscle
- PMID: 35937621
- PMCID: PMC9345755
- DOI: 10.1589/jpts.34.554
A macroscopic anatomical study of the appropriate palpation zone of the gluteus medius muscle
Abstract
[Purpose] Few previous studies have delimitated the palpation zone of the gluteus medius muscle with a focus on its fiber bundles. The purpose of this study was to clarify the morphological characteristics of the gluteus medius muscle using an anatomical approach, and to define its proper palpation zone. [Participants and Methods] In this study, we evaluated thirteen halves of the pelvic region in seven formalin-fixed cadavers. We identified the borders between the iliotibial band and gluteus medius muscle, and between the gluteus medius and gluteus maximus muscles, on the iliac crest. Furthermore, we quantified the border points of the gluteus medius' fiber bundles and observed its anatomical and morphological characteristics. [Results] We identified two fiber bundles in the gluteus medius muscle, an anterior and a posterior fiber bundle, and detected that a portion of the posterior fibers was located subcutaneously. [Conclusion] We propose that the region where the posterior fibers of the gluteus medius muscle are located subcutaneously is an appropriate zone for the palpation of this muscle.
Keywords: Gluteus medius; Gross anatomy; Palpation.
2022©by the Society of Physical Therapy Science. Published by IPEC Inc.
Figures
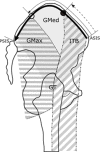
 : The iliac crest length: the length of the iliac crest from the anterior superior
iliac spine (ASIS) to the posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) along the iliac
crest.
: The iliac crest length: the length of the iliac crest from the anterior superior
iliac spine (ASIS) to the posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) along the iliac
crest.  : LAIB; The length from the ASIS to the posterior edge of the ITB.
: LAIB; The length from the ASIS to the posterior edge of the ITB.  : LAGM; The length from the ASIS to the anterior edge of the GMax. GT: Great trochanter.
: LAGM; The length from the ASIS to the anterior edge of the GMax. GT: Great trochanter.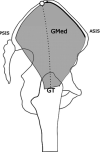
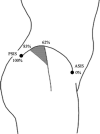
 : LAFB; The length from ASIS to 〇
: LAFB; The length from ASIS to 〇

References
-
- Bailey R, Selfe J, Richards J: The role of the Trendelenburg Test in the examination of gait. Phys Ther Rev, 2009, 14: 190–197.
-
- Katanazaka F, Kusunoki T, Hayata T, et al. : Influence of change in weight load during hip extension and abduction on electromyographic activities of the gluteus medius and maximus fibers. Rigakuryoho Kagaku, 2018, 33: 121–126.
-
- Dostal WF, Soderberg GL, Andrews JG: Actions of hip muscles. Phys Ther, 1986, 66: 351–361. - PubMed
-
- Conneely M, O Sullivan K, Edmondston S: Dissection of gluteus maximus and medius with respect to their suggested roles in pelvic and hip stability: implications for rehabilitation? Phys Ther Sport, 2006, 7: 176–178.
-
- Fredericson M, Cookingham CL, Chaudhari AM, et al. : Hip abductor weakness in distance runners with iliotibial band syndrome. Clin J Sport Med, 2000, 10: 169–175. - PubMed

