Rise of syphilis surge amidst COVID-19 pandemic in the USA: A neglected concern
- PMID: 35937637
- PMCID: PMC9339075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104239
Rise of syphilis surge amidst COVID-19 pandemic in the USA: A neglected concern
Abstract
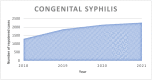
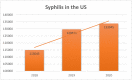
Introduction: Syphilis is a treatable but highly contagious sexually transmitted disease (STI) that has a long history of infecting millions of people from diverse ethnicities and is mainly considered promiscuity. An uprise in syphilis cases is noted in the Coronavirus pandemic. This short communication discerns salient factors precipitating the syphilis upsurge, implications, current efforts, and recommendations.
Discussion: A decrease in funds and investments for public health clinics during COVID-19 because the funds have been diverted for treating COVID-19 has resulted in a dramatic rise in syphilis. The main determinants of the increased spread of syphilis during the COVID-19 pandemic include unsafe sexual activities, reduced STI screening, lack of sufficient staff during the pandemic, and abandoning of STI programs and services.
Recommendations: We recommend high-risk screening clinics and effective telehealth programs to combat against rising STI burden in the US.
Keywords: COVID-19; Outbreak; Pandemic; Surge; Syphilis.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicting interests.
Figures
References
-
- A new study highlights an unacceptably high global prevalence of syphilis among men who have sex with men [Internet]. [cited 2021 Dec 5]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news/item/09-07-2021-new-study-highlights-unacceptab....
-
- Rise of syphilis in the U.S reflects neglect of long-term public health funding : Shots. Health News Nat. 2021 [Internet]. [cited 2021 Dec 5]. Available from: https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2021/11/01/1050568646/syphilis....
-
- Dong E., Du H., Gardner L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real-time. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020 May 1;20(5):533–534. http://www.thelancet.com/article/S1473309920301201/fulltext - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources