Sensitive and visual identification of Chlamydia trachomatis using multiple cross displacement amplification integrated with a gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor for point-of-care use
- PMID: 35937700
- PMCID: PMC9355032
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.949514
Sensitive and visual identification of Chlamydia trachomatis using multiple cross displacement amplification integrated with a gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor for point-of-care use
Abstract
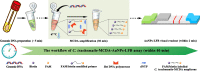
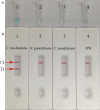
Chlamydia trachomatis is the leading cause of bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI) and remains a major public health challenge, especially in less-developed regions. Establishing a rapid, inexpensive, and easy-to-interpret point-of-care (POC) testing system for C. trachomatis could be critical for its treatment and limiting further transmission. Here, we devised a novel approach termed a multiple cross displacement amplification integrated with gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor (MCDA-AuNPs-LFB) for the highly specific, sensitive, user-friendly, and rapid identification of C. trachomatis in clinical samples. A suite of MCDA primers based on the C. trachomatis ompA gene from 14 serological variants (serovar A-K, L1, L2, and L3) were successfully designed and used to establish the assay. Optimal assay conditions were identified at 67°C, and the detection procedure, including nucleic acid preparation (approximately 5 min), MCDA amplification (30 min), and AuNPs-LFB visual readout (within 2 min), was completed within 40 min. The all-in cost for each test was approximately $5.5 USD. The limit of detection (LoD) was 10 copies/reaction, and no cross-reaction was observed with non-C. trachomatis microbes. A total of 135 suspected C. trachomatis-infection genital secretion samples were collected and simultaneously detected using real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) in our assay. Compared with the qPCR technology, the MCDA-AuNPs-LFB sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value were 100%, 96.20%, 94.92%, and 100%, respectively. Hence, our MCDA-AuNP-LFB assay exhibited considerable potential for POC testing and could be used to identify C. trachomatis in clinical settings, particularly in low-income regions.
Keywords: Chlamydia trachomatis; gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor; isothermal amplification; multiple cross displacement amplification; point-of-care testing.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Yuan, Zhou, Tan, Wang and Dong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle-based biosensor integrated with multiple cross-displacement amplification for visual and rapid identification of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 May 6;13(5):e0173824. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01738-24. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40231683 Free PMC article.
-
Visual and rapid identification of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae using multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification and a gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Feb 28;13:1067554. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1067554. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36926514 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Biosensor Integrated With Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification for Rapid and Visual Identification of Chlamydia trachomatis for Point-of-Care Use.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jul 12;13:914620. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.914620. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35903464 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid point of care test for detecting urogenital Chlamydia trachomatis infection in nonpregnant women and men at reproductive age.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 29;1(1):CD011708. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011708.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 31995238 Free PMC article.
-
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Coupled With Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Biosensor for Rapid, Sensitive, and Specific Detection of Bordetella pertussis.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Feb 8;9:797957. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.797957. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35211469 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple cross displacement amplification combined with nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of Epstein-Barr virus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jan 8;13:1321394. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1321394. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38259964 Free PMC article.
-
Gold nanoparticles-based biosensors: pioneering solutions for bacterial and viral pathogen detection-a comprehensive review.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 16;40(9):269. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-04072-1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39009934 Review.
References
-
- Buder S., Schöfer H., Meyer T., Bremer V., Kohl P. K., Skaletz-Rorowski A., et al. . (2019). J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 17 (3), 287–315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

