Dual protective role of velutin against articular cartilage degeneration and subchondral bone loss via the p38 signaling pathway in murine osteoarthritis
- PMID: 35937813
- PMCID: PMC9354239
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.926934
Dual protective role of velutin against articular cartilage degeneration and subchondral bone loss via the p38 signaling pathway in murine osteoarthritis
Abstract
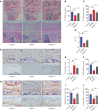
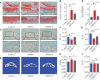
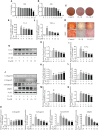
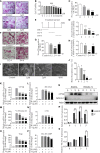
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common degenerative joint condition associated with inflammation and characterized by progressive degradation of the articular cartilage and subchondral bone loss in the early stages. Inflammation is closely associated with these two major pathophysiological changes in OA. Velutin, a flavonoid family member, reportedly exerts anti-inflammatory effects. However, the therapeutic effects of velutin in OA have not yet been characterized. In this study, we explore the effects of velutin in an OA mouse model. Histological staining and micro-CT revealed that velutin had a protective effect against cartilage degradation and subchondral bone loss in an OA mouse model generated by surgical destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM). Additionally, velutin rescued IL-1β-induced inflammation in chondrocytes and inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vitro. Mechanistically, the p38 signaling pathway was found to be implicated in the inhibitory effects of velutin. Our study reveals the dual protective effects of velutin against cartilage degradation and subchondral bone loss by inhibiting the p38 signaling pathway, thereby highlighting velutin as an alternative treatment for OA.
Keywords: chondrocyte; osteoarthritis; p38 pathway; subchondral bone; velutin.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Lu, Li, Zhang, Xu, Lou, Wang, Zhang and Qian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Subchondral osteoclasts and osteoarthritis: new insights and potential therapeutic avenues.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Apr 25;56(4):499-512. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024017. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 38439665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VX-11e protects articular cartilage and subchondral bone in osteoarthritis by inhibiting the RIP1/RIP3/MLKL and MAPK signaling pathways.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Mar;120:105632. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105632. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 35074577
-
Sotrastaurin, a PKC inhibitor, attenuates RANKL-induced bone resorption and attenuates osteochondral pathologies associated with the development of OA.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Aug;24(15):8452-8465. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15404. Epub 2020 Jul 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32652826 Free PMC article.
-
Diosmetin inhibits subchondral bone loss and indirectly protects cartilage in a surgically-induced osteoarthritis mouse model.Chem Biol Interact. 2023 Jan 25;370:110311. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110311. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Chem Biol Interact. 2023. PMID: 36563736
-
Chondrocyte Apoptosis in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Oct 30;16(11):26035-54. doi: 10.3390/ijms161125943. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26528972 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Subchondral osteoclasts and osteoarthritis: new insights and potential therapeutic avenues.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Apr 25;56(4):499-512. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024017. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 38439665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HBP-A Attenuates Knee Osteoarthritis Progression via MLK3/P38/HDAC4 Axis-Mediated Dual Protection of Articular Cartilage and Quadriceps.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 May;29(9):e70577. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70577. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40318007 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory dynamics of Nanog in chondrocyte dedifferentiation: role of KLF4/p53 and p38/AKT signaling.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Mar 11;25(1):58. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01572-7. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40067510
-
Osteoarthritis in the Elderly Population: Preclinical Evidence of Nutrigenomic Activities of Flavonoids.Nutrients. 2023 Dec 28;16(1):112. doi: 10.3390/nu16010112. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38201942 Free PMC article.
-
Application of polydopamine-modified triphasic PLA/PCL-PLGA/Mg(OH)2-velvet antler polypeptides scaffold loaded with fibrocartilage stem cells for the repair of osteochondral defects.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Sep 19;12:1460623. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1460623. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39372430 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

