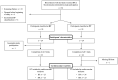
Alpha-Adrenergic Mechanisms in the Cardiovascular Hyperreactivity to Norepinephrine-Infusion in Essential Hypertension
- PMID: 35937820
- PMCID: PMC9355707
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.824616
Alpha-Adrenergic Mechanisms in the Cardiovascular Hyperreactivity to Norepinephrine-Infusion in Essential Hypertension
Abstract
Aims: Essential hypertension (EHT) is characterized by cardiovascular hyperreactivity to stress but underlying mechanism are not fully understood. Here, we investigated the role of α-adrenergic receptors (α-AR) in the cardiovascular reactivity to a norepinephrine (NE)-stress reactivity-mimicking NE-infusion in essential hypertensive individuals (HT) as compared to normotensive individuals (NT).
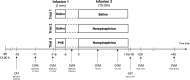
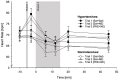
Methods: 24 male HT and 24 male NT participated in three experimental trials on three separate days with a 1-min infusion followed by a 15-min infusion. Trials varied in infusion-substances: placebo saline (Sal)-infusions (trial-1:Sal+Sal), NE-infusion without (trial-2:Sal+NE) or with non-selective α-AR blockade by phentolamine (PHE) (trial-3:PHE+NE). NE-infusion dosage (5µg/ml/min) and duration were chosen to mimic duration and physiological effects of NE-release in reaction to established stress induction protocols. We repeatedly measured systolic (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) as well as heart rate before, during, and after infusions.
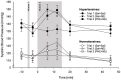
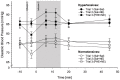
Results: SBP and DBP reactivity to the three infusion-trials differed between HT and NT (p's≤.014). HT exhibited greater BP reactivity to NE-infusion alone compared to NT (trial-2-vs-trial-1: p's≤.033). Group differences in DBP reactivity to NE disappeared with prior PHE blockade (trial-3: p=.26), while SBP reactivity differences remained (trial-3: p=.016). Heart rate reactivity to infusion-trials did not differ between HT and NT (p=.73).
Conclusion: Our findings suggest a mediating role of α-AR in DBP hyperreactivity to NE-infusion in EHT. However, in SBP hyperreactivity to NE-infusion in EHT, the functioning of α-AR seems impaired suggesting that the SBP hyperreactivity in hypertension is not mediated by α-AR.
Keywords: alpha-adrenergic receptor blockade; cardiovascular reactivity; essential hypertension; norepinephrine-infusion; phentolamine.
Copyright © 2022 Walther, von Känel, Heimgartner, Zuccarella-Hackl, Stirnimann and Wirtz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hyperreactivity of Salivary Alpha-Amylase to Acute Psychosocial Stress and Norepinephrine Infusion in Essential Hypertension.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 21;10(7):1762. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071762. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35885066 Free PMC article.
-
Norepinephrine infusion with and without alpha-adrenergic blockade by phentolamine increases salivary alpha amylase in healthy men.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2014 Nov;49:290-8. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.07.023. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2014. PMID: 25128931 Clinical Trial.
-
Prothrombotic response to norepinephrine infusion, mimicking norepinephrine stress-reactivity effects, is partly mediated by α-adrenergic mechanisms.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019 Jul;105:44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.09.018. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30318393 Clinical Trial.
-
Pathogenetic and therapeutic relevance of cardiovascular pressor reactivity to norepinephrine in human hypertension.Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1989;11 Suppl 1:257-73. doi: 10.3109/10641968909045430. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1989. PMID: 2663249 Review.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid norepinephrine levels in essential hypertension: effects of drug treatment and withdrawal.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1987;10 Suppl 12:S205-10. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1987. PMID: 2455180 Review.
Cited by
-
Pro-arrhythmic role of adrenergic spatial densities in the human atria: An in-silico study.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 25;18(8):e0290676. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290676. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37624832 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological reactivity to acute mental stress in essential hypertension-a systematic review.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Aug 11;10:1215710. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1215710. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37636310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute mental stress-induced alpha or beta-adrenergic reactivity patterns linked to unique cardiometabolic risk profiles.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 13;15(1):8668. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92961-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40082568 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperreactivity of Salivary Alpha-Amylase to Acute Psychosocial Stress and Norepinephrine Infusion in Essential Hypertension.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 21;10(7):1762. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071762. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35885066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nyklíček I, Bosch JA, Amerongen AVN. A Generalized Physiological Hyperreactivity to Acute Stressors in Hypertensives. Biol Psychol (2005) 70(1):44–51. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2004.11.013 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

