Clinical advantages and neuroprotective effects of monitor guided fang's capillary fascia preservation right RLN dissection technique
- PMID: 35937827
- PMCID: PMC9353769
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.918741
Clinical advantages and neuroprotective effects of monitor guided fang's capillary fascia preservation right RLN dissection technique
Abstract
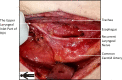
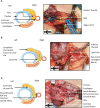
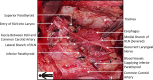
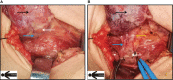
Objective: To investigate the feasibility and advantages of Fang's capillary fascia preservation right recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) dissection technique (F-R-RLN dissection) with preservation of the capillary network and fascia between the RLN and common carotid artery for greater neuroprotective efficiency compared with traditional techniques.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 102 patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma undergoing right level VI lymph node dissection in our department from March 2021 to January 2022. Sixty patients underwent F-R-RLN dissection (the experimental group) and 42 patients underwent standard dissection (the control group). The intraoperative electrical signal amplitude ratios of the RLN, the number of dissected lymph nodes, and the preservation rates of the parathyroid glands were recorded and compared between the two groups.
Results: The electrical signal amplitude ratio of the lower neck part point of the RLN to the upper laryngeal inlet point in the experimental group was significantly lower than the ratio in the control group (p = 0.006, Z-score = -2.726). One patient suffered transient RLN paralysis in both groups, but this resolved within 1 month after operation. There were no significant differences between the two groups in terms of the number of level VIa or level VIb lymph nodes dissected, nor in the rate of preservation of the parathyroid glands.
Conclusions: F-R-RLN dissection is a thorough dissection technique that is effective at preventing an electrical signal amplitude decrease in the RLN, and at preventing RLN paralysis by preserving its blood supply.
Keywords: lymph node dissection; neuroprotective; parathyroid preservation; recurrent laryngeal nerve; thyroid cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Shi, Xu, Fang, Zhong, Chen, Hou, Ma, Feng, He, Lian and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Preliminary analysis of neuroprotective effects of capillary fascia preservation recurrent laryngeal nerve anatomical method in right level Ⅵ dissection].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2023 Oct 31;103(40):3180-3185. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20230619-01040. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37879871 Chinese.
-
[Prospective analysis of the risk factors and clinical indications of dissection of lymph node posterior to right recurrent laryngeal nerve in 283 cases of papillary thyroid carcinoma].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2014 Feb;36(2):109-14. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24796458 Chinese.
-
Technique and surgical outcomes of mesenterization and intra-operative neural monitoring to reduce recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis after thoracoscopic esophagectomy: A cohort study.Int J Surg. 2018 Aug;56:301-306. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.05.738. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Int J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29879478
-
A Review of Methods for the Preservation of Laryngeal Nerves During Thyroidectomy.Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2018 Jun 18;52(2):79-91. doi: 10.14744/SEMB.2018.37928. eCollection 2018. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2018. PMID: 32595378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is there a role for intraoperative recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring during high mediastinal lymph node dissection in three-stage oesophagectomy for oesophageal cancer?Int J Surg. 2013;11(5):370-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2013.03.011. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Int J Surg. 2013. PMID: 23557980 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

