Assessing the Association Between Lead Pollution and Risk of Alzheimer's Disease by Integrating Multigenomics
- PMID: 35937890
- PMCID: PMC9353516
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.880105
Assessing the Association Between Lead Pollution and Risk of Alzheimer's Disease by Integrating Multigenomics
Abstract
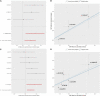
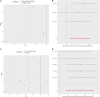
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a life-threatening neurodegenerative disease of the elderly. In recent observations, exposure to heavy metals environmental may increase the risk of AD. However, there are few studies on the causal relationship between heavy metal exposure and AD. In this study, we integrated two large-scale summaries of AD genome-wide association study (GWAS) datasets and a blood lead level GWAS dataset and performed the two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis to assess the causality of blood lead level and AD risk. The results showed that there is a significantly positive causality between blood lead level and AD risk both in the inverse-variance weighted (IVW) model and the weighted median estimator (WME) model. An independent additional verification also reached a consistent conclusion. These findings further confirm the conclusions of previous studies and improve the understanding of the relationship between AD pathogenesis and the toxicity of lead in environmental pollution.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Mendelian randomization; blood lead; heavy metal pollution; multigenomics.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Zhang, Liang, Wu and Zou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metals in Alzheimer's Disease.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 12;11(4):1161. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041161. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multigenomics Reveals the Causal Effect of Herpes Simplex Virus in Alzheimer's Disease: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 5;12:773725. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.773725. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35069681 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Mendelian Randomization Study.Front Neurosci. 2018 Sep 12;12:627. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00627. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30258348 Free PMC article.
-
Life Course Adiposity and Alzheimer's Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;82(2):503-512. doi: 10.3233/JAD-210345. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 34057091
-
An Updated Mendelian Randomization Analysis of the Association Between Serum Calcium Levels and the Risk of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Genet. 2021 Sep 8;12:731391. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.731391. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34567081 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Post-mortem human Alzheimer´s brain metallome depends on Braak stages and brain regions.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20709. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08143-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595297 Free PMC article.
-
Metals in Alzheimer's Disease.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 12;11(4):1161. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041161. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189779 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

