Managing SARS-CoV2 Infections Through Resolution of Inflammation by Eicosanoids: A Review
- PMID: 35937919
- PMCID: PMC9346295
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S355568
Managing SARS-CoV2 Infections Through Resolution of Inflammation by Eicosanoids: A Review
Abstract
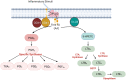
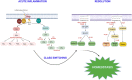
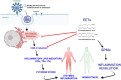
Severe Corona Virus Disease is characterized by angiocentric inflammation of lungs and cytokine storm leading to potentially fatal multiple organ failure. Several studies have shown the high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, indicative of a poor prognosis in COVID-19. Eicosanoids play an important role in the induction of inflammation and cytokine production, while anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving properties of some eicosanoic acid derivatives enable inflamed tissues to return to homeostasis through the resolution of inflammation by aiding the clearance of cell debris and downregulation of pro-inflammatory stimulants. This review attempts to provide an overall insight on the eicosanoids synthesis and their role in the resolution of inflammation in the context of Corona Virus infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; cyclooxygenases; cytochrome P450; eicosanoids; lipid mediators of inflammation; lipoxygenases; polyunsaturated fatty acids.
© 2022 Mohammed et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammation resolution: a dual-pronged approach to averting cytokine storms in COVID-19?Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020 Jun;39(2):337-340. doi: 10.1007/s10555-020-09889-4. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020. PMID: 32385712 Free PMC article.
-
Specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators regulate inflammatory macrophages: A paradigm shift from antibiotics to immunotherapy for mitigating COVID-19 pandemic.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Feb 3;10:1104577. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1104577. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36825200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eicosanoids in inflammation in the blood and the vessel.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 27;13:997403. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.997403. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36238558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specialized pro-resolving mediators: biosynthesis and biological role in bacterial infections.FEBS J. 2022 Jul;289(14):4212-4227. doi: 10.1111/febs.16266. Epub 2021 Nov 18. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34741578 Review.
-
Stimulating the Resolution of Inflammation Through Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in COVID-19: Rationale for the COVID-Omega-F Trial.Front Physiol. 2021 Jan 11;11:624657. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.624657. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33505321 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitor, Zileuton, Modulates Host Immune Responses and Improves Lung Function in a Model of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Induced by Betacoronavirus.Viruses. 2023 Oct 4;15(10):2049. doi: 10.3390/v15102049. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37896826 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Effects of 3-epi-betulin from Daphniphyllum glaucescens in Suppressing SARS-CoV-2-Induced Inflammation and Inhibiting Virus Entry.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 1;24(23):17040. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317040. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069363 Free PMC article.
-
Crystalline silica-induced proinflammatory eicosanoid storm in novel alveolar macrophage model quelled by docosahexaenoic acid supplementation.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 9;14:1274147. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1274147. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022527 Free PMC article.
-
BCG vaccination is associated with longitudinal changes in systemic eicosanoid levels in elderly individuals: A secondary outcome analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 11;10(12):e32643. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32643. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38975122 Free PMC article.
-
Treating COVID-19 with Medicinal Plants: Is It Even Conceivable? A Comprehensive Review.Viruses. 2024 Feb 20;16(3):320. doi: 10.3390/v16030320. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38543686 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

