Oxidative Stress-Induced Protein of SESTRIN2 in Cardioprotection Effect
- PMID: 35937943
- PMCID: PMC9355779
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7439878
Oxidative Stress-Induced Protein of SESTRIN2 in Cardioprotection Effect
Abstract
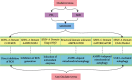
Because of the rich mitochondria and high energy metabolic requirements, excessive oxidative stress generated by ROS is a key pathogenic mechanism in heart disease. SESTRIN2, the well-known antioxidant protein, plays a vital role in diminishing the production and accumulation of ROS, thus sparing cells from oxidative damage. From this new perspective, we first examine SESTRIN2 structure-function relationships; then, we describe how SESTRIN2 expression is regulated under oxidative stress conditions, emphasizing SESTRIN2's antioxidant mechanism via multiple signal transductions; and finally, we discuss SESTRIN2's role in a variety of oxidative stress-related cardiac diseases, including age-related heart disease, diabetic cardiomyopathy, ischemia-reperfusion myocardial injury, septic cardiomyopathy, and chronic cardiac insufficiency. The goal of this review is to identify the SESTRIN2 protein as a potential biomarker and new therapy target for oxidative stress-related cardiac diseases.
Copyright © 2022 Huang Rongjin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Griendling K. K., Touyz R. M., Zweier J. L., et al. Measurement of reactive oxygen species, reactive nitrogen species, and redox-dependent signaling in the cardiovascular system: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation Research . 2016;119(5):e39–e75. doi: 10.1161/RES.0000000000000110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

