Identification and Validation of Cuproptosis-Related Prognostic Signature and Associated Regulatory Axis in Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma
- PMID: 35937995
- PMCID: PMC9353190
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.912037
Identification and Validation of Cuproptosis-Related Prognostic Signature and Associated Regulatory Axis in Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma
Abstract
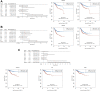
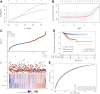
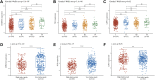
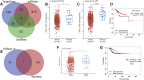
Background: Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma (UCEC) is a common gynecological malignancy globally with high recurrence and mortality rates. Cuproptosis is a new type of programmed cell death involved in tumor cell proliferation and growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Methods: The difference in cuproptosis-related genes (CRGs) between UCEC tissues and normal tissues deposited in The Cancer Genome Atlas database was calculated using the "limma" R package. LASSO Cox regression analysis was conducted to construct a prognostic cuproptosis-related signature. Kaplan-Meier analysis was conducted to compare the survival of UCEC patients. A ceRNA network was constructed to identify the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory axis. Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed to verify CRG expression in UCEC. Results: The expression of FDX1, LIAS, DLAT, and CDKN2A were upregulated, whereas the expression of LIPT1, DLD, PDHB, MTF1, and GLS were downregulated in UCEC versus normal tissues. The genetic mutation landscape of CRGs in UCEC was also summarized. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analyses revealed that these CRGs were enriched in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, glycolysis, and HIF-1 signaling pathway. LASSO Cox regression analysis was performed and identified a cuproptosis-related prognostic signature including these three prognostic biomarkers (CDKN2A, GLS, and LIPT1). UCEC patients with high risk scores had a poor prognosis with an area under the curve of 0.782 and 0.764 on 3- and 5-year receiver operating characteristic curves. Further analysis demonstrated a significant correlation between CDKN2A and pTNM stage, tumor grade, immune cell infiltration, drug sensitivity, tumor mutational burden (TMB) score, and microsatellite instable (MSI) score. The data validation of qRT-PCR further demonstrated the upregulation of CDKN2A and the downregulation of LIPT1 and GLS in UCEC versus normal tissues. The ceRNA network also identified lncRNA XIST/miR-125a-5p/CDKN2A regulatory axis for UCEC. Conclusion: The current study identified a cuproptosis-related prognostic signature including these three prognostic biomarkers (CDKN2A, GLS, and LIPT1) for UCEC. The ceRNA network also identified that lncRNA XIST/miR-125a-5p/CDKN2A regulatory axis may be involved in the progression of UCEC. Further in vivo and in vitro studies should be conducted to verify these results.
Keywords: CDKN2A; cuproptosis; immunotherapy; prognostic signature; uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma.
Copyright © 2022 Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Database Mining Detected a Cuproptosis-Related Prognostic Signature and a Related Regulatory Axis in Breast Cancer.Dis Markers. 2022 Oct 19;2022:9004830. doi: 10.1155/2022/9004830. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 36312586 Free PMC article.
-
Cuproptosis-Related Genes MTF1 and LIPT1 as Novel Prognostic Biomarker in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Biochem Genet. 2024 Apr;62(2):1136-1159. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10473-y. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 37561332
-
A cuproptosis-related gene signature and associated regulatory axis in stomach adenocarcinoma based on bioinformatics analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jul 28;102(30):e34230. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034230. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37505170 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel cuproptosis-related gene signature and integrative analyses in patients with lower-grade gliomas.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 15;13:933973. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.933973. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36045691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC01589 serves as a potential tumor-suppressor and immune-related biomarker in endometrial cancer: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Apr 14;102(15):e33536. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033536. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37058060 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Copper homeostasis and cuproptosis in tumor pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 12;14:1271613. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1271613. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37767404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of the cuproptosis-related gene DLD across cancers: A potential prognostic and immunotherapeutic target.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 3;14:1111462. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1111462. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37113760 Free PMC article.
-
The crosstalk role of CDKN2A between tumor progression and cuproptosis resistance in colorectal cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jun 17;16(12):10512-10538. doi: 10.18632/aging.205945. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38888512 Free PMC article.
-
A novel cuproptosis-related lncRNAs signature predicts prognostic and immune of bladder urothelial carcinoma.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 31;14:1148430. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1148430. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37065485 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Prognosis and Chemotherapeutic Sensitivity Based on Cuproptosis-Associated lncRNAs in Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Endocervical Adenocarcinoma.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jun 30;14(7):1381. doi: 10.3390/genes14071381. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510286 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

