Prognostic Signature and Tumor Immune Landscape of N7-Methylguanosine-Related lncRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 35938009
- PMCID: PMC9354608
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.906496
Prognostic Signature and Tumor Immune Landscape of N7-Methylguanosine-Related lncRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
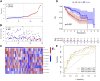
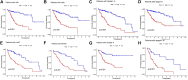
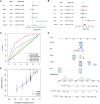
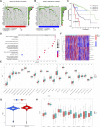
Despite great advances in the treatment of liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC), such as immunotherapy, the prognosis remains extremely poor, and there is an urgent need to develop novel diagnostic and prognostic markers. Recently, RNA methylation-related long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been demonstrated to be novel potential biomarkers for tumor diagnosis and prognosis as well as immunotherapy response, such as N6-methyladenine (m6A) and 5-methylcytosine (m5C). N7-Methylguanosine (m7G) is a widespread RNA modification in eukaryotes, but the relationship between m7G-related lncRNAs and prognosis of LIHC patients as well as tumor immunotherapy response is still unknown. In this study, based on the LIHC patients' clinical and transcriptomic data from TCGA database, a total of 992 m7G-related lncRNAs that co-expressed with 22 m7G regulatory genes were identified using Pearson correlation analysis. Univariate regression analysis was used to screen prognostic m7G-related lncRNAs, and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) and multivariate Cox regression were applied to construct a 9-m7G-related-lncRNA risk model. The m7G-related lncRNA risk model was validated to exhibit good prognostic performance through Kaplan-Meier analysis and ROC analysis. Together with the clinicopathological features, the m7G-related lncRNA risk score was found to be an independent prognostic factor for LIHC. Furthermore, the high-risk group of LIHC patients was unveiled to have a higher tumor mutation burden (TMB), and their tumor microenvironment was more prone to the immunosuppressive state and exhibited a lower response rate to immunotherapy. In addition, 47 anti-cancer drugs were identified to exhibit a difference in drug sensitivity between the high-risk and low-risk groups. Taken together, the m7G-related lncRNA risk model might display potential value in predicting prognosis, immunotherapy response, and drug sensitivity in LIHC patients.
Keywords: LIHC; immune response; lncRNA; m7G methylation; prognostic model.
Copyright © 2022 Wei, Liu, Wang, Jiang, Wang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Construction and validation of a prognostic signature for mucinous colonic adenocarcinoma based on N7-methylguanosine-related long non-coding RNAs.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Feb 29;15(1):203-219. doi: 10.21037/jgo-23-980. Epub 2024 Feb 28. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38482248 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of prognostic signature of breast cancer based on N7-Methylguanosine-Related LncRNAs and prediction of immune response.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 24;13:991162. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.991162. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36353118 Free PMC article.
-
Constructing and validating of m7G-related genes prognostic signature for hepatocellular carcinoma and immune infiltration: potential biomarkers for predicting the overall survival.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Dec;13(6):3169-3182. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-1134. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36636051 Free PMC article.
-
The lncRNA epigenetics: The significance of m6A and m5C lncRNA modifications in cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 9;13:1063636. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1063636. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36969033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of RNA modification in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 2;13:984453. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.984453. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36120301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging role of RNA modification and long noncoding RNA interaction in cancer.Cancer Gene Ther. 2024 Jun;31(6):816-830. doi: 10.1038/s41417-024-00734-2. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 38351139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A methylation- and immune-related lncRNA signature to predict ovarian cancer outcome and uncover mechanisms of chemoresistance.J Ovarian Res. 2023 Sep 6;16(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01260-9. J Ovarian Res. 2023. PMID: 37674251 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of an m7G-related lncRNAs signature for predicting prognosis, immune response and therapy landscapes in ovarian cancer.Front Genet. 2024 Oct 8;15:1466422. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1466422. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39440245 Free PMC article.
-
RNA modifications in cancer.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jan 10;6(1):e70042. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70042. eCollection 2025 Jan. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 39802639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis of N7-methylguanosine regulators: Expression features and potential implications in prognosis and immunotherapy.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 21;13:1016797. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1016797. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36339001 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

