Novel angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from tuna byproducts-milts: Preparation, characterization, molecular docking study, and antioxidant function on H2O2-damaged human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- PMID: 35938100
- PMCID: PMC9355146
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.957778
Novel angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from tuna byproducts-milts: Preparation, characterization, molecular docking study, and antioxidant function on H2O2-damaged human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Abstract
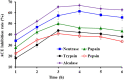
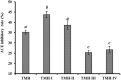
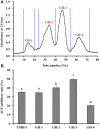
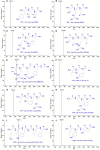
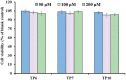
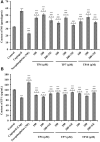
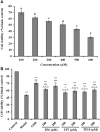
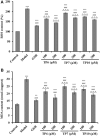
To prepare peptides with high angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory (ACEi) activity, Alcalase was screened from five proteases and employed to prepare protein hydrolysate (TMH) of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) milts. Subsequently, 10 novel ACEi peptides were isolated from the high-ACEi activity TMH and identified as Tyr-Asp-Asp (YDD), Thr-Arg-Glu (TRE), Arg-Asp-Tyr (RDY), Thr-Glu-Arg-Met (TERM), Asp-Arg-Arg-Tyr-Gly (DRRYG), Ile-Cys-Tyr (ICY), Leu-Ser-Phe-Arg (LSFR), Gly-Val-Arg-Phe (GVRF), Lys-Leu-Tyr-Ala-Leu-Phe (KLYALF), and Ile-Tyr-Ser-Pro (IYSP) with molecular weights of 411.35, 404.41, 452.45, 535.60, 665.69, 397.48, 521.61, 477.55, 753.91, and 478.53 Da, respectively. Among them, the IC50 values of ICY, LSFR, and IYSP on ACE were 0.48, 0.59, and 0.76 mg/mL, respectively. The significant ACEi activity of ICY, LSFR, and IYSP with affinities of -7.0, -8.5, and -8.3 kcal/mol mainly attributed to effectively combining with the ACEi active sites through hydrogen bonding, electrostatic force, and hydrophobic interaction. Moreover, ICY, LSFR, and IYSP could positively influence the production of nitric oxide (NO) and endothelin-1 (ET-1) secretion in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and weaken the adverse impact of norepinephrine (NE) on the production of NO and ET-1. In addition, ICY, LSFR, and IYSP could provide significant protection to HUVECs against H2O2 damage by increasing antioxidase levels to decrease the contents of reactive oxide species and malondialdehyde. Therefore, the ACEi peptides of ICY, LSFR, and IYSP are beneficial functional molecules for healthy foods against hypertension and cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE); antihypertensive function; antioxidant activity; milt; peptide; skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis).
Copyright © 2022 Suo, Zheng, Chi, Luo and Wang.
Figures


References
-
- Auwal SM, Zainal Abidin N, Zarei M, Tan CP, Saari N. Identification, structure-activity relationship and in silico molecular docking analyses of five novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides from stone fish (Actinopyga lecanora) hydrolysates. PLoS ONE. (2019) 14:e0197644. 10.1371/journal.pone.0197644 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Suo SK, Zhao YQ, Wang YM, Pan XY, Chi CF, Wang B. Seventeen novel angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from protein hydrolysate of Mytilus edulis: isolation, identification, molecular docking study, and protective function on HUVECs. Food Funct. (2022). 10.1039/D2FO00275B (In Press) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abdelhedi O, Nasri M. Basic and recent advances in marine antihypertensive peptides: production, structure-activity relationship and bioavailability. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2019) 88:543–57. 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.04.002 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

