The Pulsed Electric Field Assisted-Extraction Enhanced the Yield and the Physicochemical Properties of Soluble Dietary Fiber From Orange Peel
- PMID: 35938122
- PMCID: PMC9355398
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.925642
The Pulsed Electric Field Assisted-Extraction Enhanced the Yield and the Physicochemical Properties of Soluble Dietary Fiber From Orange Peel
Abstract
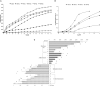
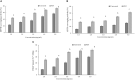
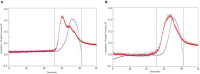
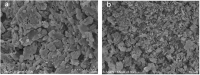
The study aimed to investigate the effects of pulsed electric field (PEF)-assisted extraction on the yield, physicochemical properties, and structure of soluble dietary fiber (SDF) from orange peel. The results showed that the optinal parameters of PEF assisted extraction SDF was temperature of 45oC with the electric field intensity of 6.0 kV/cm, pulses number of 30, and time of 20min and SDF treated with PEF showed the higher water solubility, water-holding and oil-holding capacity, swelling capacity, emulsifying activity, emulsion stability, foam stability and higher binding capacity for Pb2+, As3+, Cu2+, and higher which resulted from the higher viscosity due to PEF treatment. Compared with the untreated orange peel, the SDF obtained with PEF exhibited stronger antioxidant activities, which was due to its smaller molecular weight (189 vs. 512 kDa). In addition, scanning electron micrograph images demonstrated that the surface of PEF-SDF was rough and collapsed. Overall, it was suggested that PEF treatment could improve the physicochemical properties of SDF from the orange peel and would be the potential extraction technology with high efficiency.
Keywords: extraction; orange peel; physicochemical properties; pulsed electric field; soluble dietary fiber.
Copyright © 2022 Fan, Wang, Fan, Sun and Dong.
Conflict of interest statement
WS was employed by Beijing institute of nutritional resources Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare that this study received funding from key Science and Technology Projects of Hebei Province of China (No. 19227516D) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation - China (2019BH029). The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, and the decision to submit it for publication.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Characterization of the structural, physicochemical, and functional properties of soluble dietary fibers obtained from the peanut shell using different extraction methods.Front Nutr. 2023 Feb 1;9:1103673. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1103673. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36817066 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Peanut Shells Prepared by Pulsed Electric Fields with Three-Phase Partitioning.Molecules. 2024 Apr 3;29(7):1603. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071603. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38611882 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and physicochemical properties of soluble dietary fiber from orange peel assisted by steam explosion and dilute acid soaking.Food Chem. 2015 Oct 15;185:90-8. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.03.112. Epub 2015 Apr 3. Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 25952845
-
Pulsed Electric Field: Fundamentals and Effects on the Structural and Techno-Functional Properties of Dairy and Plant Proteins.Foods. 2022 May 25;11(11):1556. doi: 10.3390/foods11111556. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35681305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of structural characteristics on the physicochemical properties and functional activities of dietary fiber: A review of structure-activity relationship.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jun;269(Pt 2):132214. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132214. Epub 2024 May 8. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38729489 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the structural, physicochemical, and functional properties of soluble dietary fibers obtained from the peanut shell using different extraction methods.Front Nutr. 2023 Feb 1;9:1103673. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1103673. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36817066 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Wet Fractionation Conditions and Pulsed Electric Field on Arabinoxylan and Protein Recovery from Maize.Foods. 2025 Feb 23;14(5):760. doi: 10.3390/foods14050760. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40077463 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the quality of soluble dietary fiber from Poria cocos peel residue following steam explosion.Food Chem X. 2023 Aug 7;19:100829. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100829. eCollection 2023 Oct 30. Food Chem X. 2023. PMID: 37780304 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Peanut Shells Prepared by Pulsed Electric Fields with Three-Phase Partitioning.Molecules. 2024 Apr 3;29(7):1603. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071603. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38611882 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing enzymatic production efficiency of crude pectic oligosaccharides by pulsed electric field and study of prebiotic potential.J Food Sci Technol. 2024 Feb;61(2):320-330. doi: 10.1007/s13197-023-05843-8. Epub 2023 Sep 29. J Food Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 38196705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jiang N, Jin LF, Teixeira da Silva JA, IsIam MZ, Gao HW, Liu YZ, et al. . Activities of enzymes directly related with sucrose and citric acid metabolism in citrus fruit in response to soil plastic fifilm mulch. Sci Hortic. (2014) 168:73–80. 10.1016/j.scienta.2014.01.021 - DOI
-
- Marín FR, Soler-Rivas C, Benavente-García O, Castillo J, Pérez-Alvarez JA. By-products from different citrus processes as a source of customized functional fibres. Food Chem. (2007) 100:736–41. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.04.040 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

