Image enhancement techniques on deep learning approaches for automated diagnosis of COVID-19 features using CXR images
- PMID: 35938148
- PMCID: PMC9340712
- DOI: 10.1007/s11042-022-13486-8
Image enhancement techniques on deep learning approaches for automated diagnosis of COVID-19 features using CXR images
Abstract
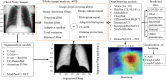
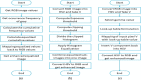
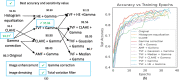
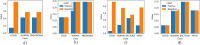
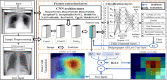
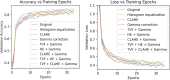
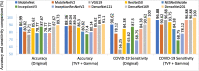
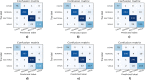
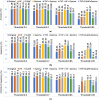
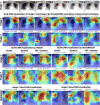
The outbreak of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) disease has infected more than 135.6 million people globally. For its early diagnosis, researchers consider chest X-ray examinations as a standard screening technique in addition to RT-PCR test. Majority of research work till date focused only on application of deep learning approaches that is relevant but lacking in better pre-processing of CXR images. Towards this direction, this study aims to explore cumulative effects of image denoising and enhancement approaches on the performance of deep learning approaches. Regarding pre-processing, suitable methods for X-ray images, Histogram equalization, CLAHE and gamma correction have been tested individually and along with adaptive median filter, median filter, total variation filter and gaussian denoising filters. Proposed study compared eleven combinations in exploration of most coherent approach in greedy manner. For more robust analysis, we compared ten CNN architectures for performance evaluation with and without enhancement approaches. These models are InceptionV3, InceptionResNetV2, MobileNet, MobileNetV2, Vgg19, NASNetMobile, ResNet101, DenseNet121, DenseNet169, DenseNet201. These models are trained in 4-way (COVID-19 pneumonia vs Viral vs Bacterial pneumonia vs Normal) and 3-way classification scenario (COVID-19 vs Pneumonia vs Normal) on two benchmark datasets. The proposed methodology determines with TVF + Gamma, models achieve higher classification accuracy and sensitivity. In 4-way classification MobileNet with TVF + Gamma achieves top accuracy of 93.25% with 1.91% improvement in accuracy score, COVID-19 sensitivity of 98.72% and F1-score of 92.14%. In 3-way classification our DenseNet201 with TVF + Gamma gains accuracy of 91.10% with improvement of 1.47%, COVID-19 sensitivity of 100% and F1-score of 91.09%. Proposed study concludes that deep learning modes with gamma correction and TVF + Gamma has superior performance compared to state-of-the-art models. This not only minimizes overlapping between COVID-19 and virus pneumonia but advantageous in time required to converge best possible results.
Keywords: COVID-19 analysis; Chest X-ray; Deep learning; Image denoising; Image enhancement; Pneumonia classification.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Exploring the effect of image enhancement techniques on COVID-19 detection using chest X-ray images.Comput Biol Med. 2021 May;132:104319. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104319. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33799220 Free PMC article.
-
Covid-MANet: Multi-task attention network for explainable diagnosis and severity assessment of COVID-19 from CXR images.Pattern Recognit. 2022 Nov;131:108826. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108826. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Pattern Recognit. 2022. PMID: 35698723 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumonia Classification Using Deep Learning from Chest X-ray Images During COVID-19.Cognit Comput. 2021 Jan 4:1-13. doi: 10.1007/s12559-020-09787-5. Online ahead of print. Cognit Comput. 2021. PMID: 33425044 Free PMC article.
-
Development and integration of VGG and dense transfer-learning systems supported with diverse lung images for discovery of the Coronavirus identity.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;32:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101004. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35822170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 diagnosis: A comprehensive review of pre-trained deep learning models based on feature extraction algorithm.Results Eng. 2023 Jun;18:101020. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101020. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Results Eng. 2023. PMID: 36945336 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 Hierarchical Classification Using a Deep Learning Multi-Modal.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 20;24(8):2641. doi: 10.3390/s24082641. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38676257 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning Approach for Biomedical Image Classification.J Imaging Inform Med. 2025 Jul 8. doi: 10.1007/s10278-025-01590-8. Online ahead of print. J Imaging Inform Med. 2025. PMID: 40627296 Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence for Early Detection of Chest Nodules in X-ray Images.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 7;10(11):2839. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112839. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36359360 Free PMC article.
-
An anatomically enhanced and clinically validated framework for lung abnormality classification using deep features and KL divergence.MethodsX. 2025 May 14;14:103348. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2025.103348. eCollection 2025 Jun. MethodsX. 2025. PMID: 40488166 Free PMC article.
-
2.5D deep learning radiomics and clinical data for predicting occult lymph node metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01759-1. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40597741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdullah-Al-Wadud M, Kabir MH, Dewan MAA, Chae O. A dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans Consum Electron. 2007;53(2):593–600. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2007.381734. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
