Focus on the tumor microenvironment: A seedbed for neuroendocrine prostate cancer
- PMID: 35938167
- PMCID: PMC9355504
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.955669
Focus on the tumor microenvironment: A seedbed for neuroendocrine prostate cancer
Abstract
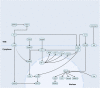
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a microecology consisting of tumor and mesenchymal cells and extracellular matrices. The TME plays important regulatory roles in tumor proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and differentiation. Neuroendocrine differentiation (NED) is a mechanism by which castration resistance develops in advanced prostate cancer (PCa). NED is induced after androgen deprivation therapy and neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC) is established finally. NEPC has poor prognosis and short overall survival and is a major cause of death in patients with PCa. Both the cellular and non-cellular components of the TME regulate and induce NEPC formation through various pathways. Insights into the roles of the TME in NEPC evolution, growth, and progression have increased over the past few years. These novel insights will help refine the NEPC formation model and lay the foundation for the discovery of new NEPC therapies targeting the TME.
Keywords: androgen deprivation therapy (ADT); castration-resistant prostate cancer; lineage plasticity; neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC); tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Zhou, He, Li, Alsharafi, Deng, Long and Gan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuroendocrine Differentiation of Prostate Cancer-An Intriguing Example of Tumor Evolution at Play.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Sep 20;11(10):1405. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101405. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31547070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment-induced neuroendocrine prostate cancer and de novo neuroendocrine prostate cancer: Identification, prognosis and survival, genetic and epigenetic factors.World J Clin Cases. 2024 May 6;12(13):2143-2146. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i13.2143. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 38808339 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MicroRNAs in Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer.Noncoding RNA. 2022 Mar 30;8(2):25. doi: 10.3390/ncrna8020025. Noncoding RNA. 2022. PMID: 35447888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Castration-Induced Downregulation of SPARC in Stromal Cells Drives Neuroendocrine Differentiation of Prostate Cancer.Cancer Res. 2021 Aug 15;81(16):4257-4274. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0163. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34185677 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Models of Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer.Curr Protoc. 2023 May;3(5):e742. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.742. Curr Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37166213 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer Drivers SOX2 and BRN2 Confer Differential Responses to Imipridones ONC201, ONC206, and ONC212 in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 30:2024.08.28.610184. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.28.610184. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Am J Transl Res. 2024 Dec 15;16(12):7972-7982. doi: 10.62347/NBNQ6383. PMID: 39257809 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
LAMP5, One of Four Genes Related to Oxidative Stress That Predict Biochemical Recurrence-Free Survival, Promotes Proliferation and Invasion in Prostate Cancer.Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2024 Nov 30;17:119-138. doi: 10.2147/AABC.S489131. eCollection 2024. Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2024. Retraction in: Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2025 Mar 06;18:1-2. doi: 10.2147/AABC.S526200. PMID: 39634037 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor as a drug target in advanced prostate cancer therapy - obstacles and perspectives.Transcription. 2025 Feb;16(1):47-66. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2024.2334106. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Transcription. 2025. PMID: 38547312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition-Related Markers in Prostate Cancer: From Bench to Bedside.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 14;15(8):2309. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082309. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
It Takes Two to Tango: The Interplay between Prostate Cancer and Its Microenvironment from an Epigenetic Perspective.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;16(2):294. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020294. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254784 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aggarwal R. R., Feng F. Y., Small E. J. (2017). Emerging categories of disease in advanced prostate cancer and their therapeutic implications. Oncol. Willist. Park) 31 (6), 467–474. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

