Blocking circadian clock factor Rev-erbα inhibits growth plate chondrogenesis via up-regulating MAPK-ERK1/2 pathway
- PMID: 35938533
- PMCID: PMC9769450
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2109106
Blocking circadian clock factor Rev-erbα inhibits growth plate chondrogenesis via up-regulating MAPK-ERK1/2 pathway
Abstract
Emerging evidence indicated circadian clock gene Rev-erbα was involved in cartilage metabolism, however the contribution of Rev-erbα to growth plate chondrogenesis remains unknown. Here, we found that Rev-erbα exhibited the spatiotemporal expression model in growth plate. Moreover, Rev-erbα antagonist SR8278 inhibited longitudinal elongation of metatarsal bone ex vivo. And morphological analysis exhibited SR8278 led to the reduced height of growth plate and hypertrophic zone. Furthermore, blocking Rev-erbα suppressed the proliferation and hypertrophic differentiation of chondrocytes in growth plate. Similarly, knock-down Rev-erbα inhibited the proliferation and differentiation of primary chondrocytes in vitro. The mechanistic study indicated that knock-down Rev-erbα up-regulated MAPK-ERK1/2 pathway in chondrocytes. However, restraint of MAPK-ERK1/2 pathway alleviated partially SR8278-inhibited longitudinal elongation of metatarsal bone and growth plate development. Therefore, our results provide evidence of the vital role of Rev-erbα on growth plate chondrogenesis.
Keywords: MAPK-ERK1/2; Rev-erbα; chondrogenesis; growth plate.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
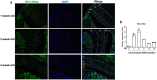

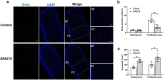
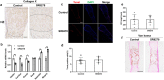



References
-
- Kronenberg HM. Developmental regulation of the growth plate. Nature. 2003;423:332–336. - PubMed
-
- Xie Y, Zhou S, Chen H, et al. Recent research on the growth plate: advances in fibroblast growth factor signaling in growth plate development and disorders. J Mol Endocrinol. 2014;53:T11–34. - PubMed
-
- Reppert SM, Weaver DR. Coordination of circadian timing in mammals. Nature. 2002;418:935–941. - PubMed
-
- Reinke H, Asher G. Crosstalk between metabolism and circadian clocks. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:227–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
