Thrombosis-related circulating miR-16-5p is associated with disease severity in patients hospitalised for COVID-19
- PMID: 35938548
- PMCID: PMC9361765
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2022.2100629
Thrombosis-related circulating miR-16-5p is associated with disease severity in patients hospitalised for COVID-19
Abstract
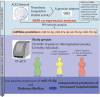
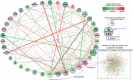
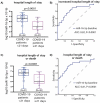
SARS-CoV-2 tropism for the ACE2 receptor, along with the multifaceted inflammatory reaction, is likely to drive the generalized hypercoagulable and thrombotic state seen in patients with COVID-19. Using the original bioinformatic workflow and network medicine approaches we reanalysed four coronavirus-related expression datasets and performed co-expression analysis focused on thrombosis and ACE2 related genes. We identified microRNAs (miRNAs) which play role in ACE2-related thrombosis in coronavirus infection and further, we validated the expressions of precisely selected miRNAs-related to thrombosis (miR-16-5p, miR-27a-3p, let-7b-5p and miR-155-5p) in 79 hospitalized COVID-19 patients and 32 healthy volunteers by qRT-PCR. Consequently, we aimed to unravel whether bioinformatic prioritization could guide selection of miRNAs with a potential of diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers associated with disease severity in patients hospitalized for COVID-19. In bioinformatic analysis, we identified EGFR, HSP90AA1, APP, TP53, PTEN, UBC, FN1, ELAVL1 and CALM1 as regulatory genes which could play a pivotal role in COVID-19 related thrombosis. We also found miR-16-5p, miR-27a-3p, let-7b-5p and miR-155-5p as regulators in the coagulation and thrombosis process. In silico predictions were further confirmed in patients hospitalized for COVID-19. The expression levels of miR-16-5p and let-7b in COVID-19 patients were lower at baseline, 7-days and 21-day after admission compared to the healthy controls (p < 0.0001 for all time points for both miRNAs). The expression levels of miR-27a-3p and miR-155-5p in COVID-19 patients were higher at day 21 compared to the healthy controls (p = 0.007 and p < 0.001, respectively). A low baseline miR-16-5p expression presents predictive utility in assessment of the hospital length of stay or death in follow-up as a composite endpoint (AUC:0.810, 95% CI, 0.71-0.91, p < 0.0001) and low baseline expression of miR-16-5p and diabetes mellitus are independent predictors of increased length of stay or death according to a multivariate analysis (OR: 9.417; 95% CI, 2.647-33.506; p = 0.0005 and OR: 6.257; 95% CI, 1.049-37.316; p = 0.044, respectively). This study enabled us to better characterize changes in gene expression and signalling pathways related to hypercoagulable and thrombotic conditions in COVID-19. In this study we identified and validated miRNAs which could serve as novel, thrombosis-related predictive biomarkers of the COVID-19 complications, and can be used for early stratification of patients and prediction of severity of infection development in an individual.Abbreviations: ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2AF, atrial fibrillationAPP, Amyloid Beta Precursor ProteinaPTT, activated partial thromboplastin timeAUC, Area under the curveAβ, amyloid betaBMI, body mass indexCAD, coronary artery diseaseCALM1, Calmodulin 1 geneCaM, calmodulinCCND1, Cyclin D1CI, confidence intervalCOPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseCOVID-19, Coronavirus disease 2019CRP, C-reactive proteinCV, CardiovascularCVDs, cardiovascular diseasesDE, differentially expressedDM, diabetes mellitusEGFR, Epithelial growth factor receptorELAVL1, ELAV Like RNA Binding Protein 1FLNA, Filamin AFN1, Fibronectin 1GEO, Gene Expression OmnibushiPSC-CMs, Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytesHSP90AA1, Heat Shock Protein 90 Alpha Family Class A Member 1Hsp90α, heat shock protein 90αICU, intensive care unitIL, interleukinIQR, interquartile rangelncRNAs, long non-coding RNAsMI, myocardial infarctionMiRNA, MiR, microRNAmRNA, messenger RNAncRNA, non-coding RNANERI, network-medicine based integrative approachNF-kB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cellsNPV, negative predictive valueNXF, nuclear export factorPBMCs, Peripheral blood mononuclear cellsPCT, procalcitoninPPI, Protein-protein interactionsPPV, positive predictive valuePTEN, phosphatase and tensin homologqPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reactionROC, receiver operating characteristicSARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2SD, standard deviationTLR4, Toll-like receptor 4TM, thrombomodulinTP53, Tumour protein P53UBC, Ubiquitin CWBC, white blood cells.
Keywords: ACE2; SARS-COV-2; bioinformatics analysis; in silico prediction; miRNA; microRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures



Similar articles
-
ACE2 Interaction Networks in COVID-19: A Physiological Framework for Prediction of Outcome in Patients with Cardiovascular Risk Factors.J Clin Med. 2020 Nov 21;9(11):3743. doi: 10.3390/jcm9113743. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33233425 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of circulating ACE2-network related microRNAs in patients with COVID-19.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 12;14(1):13573. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58037-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38866792 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Analysis of Targeting SARS-CoV-2, Viral Entry Proteins ACE2 and TMPRSS2, and Interferon Genes by Host MicroRNAs.Genes (Basel). 2020 Nov 16;11(11):1354. doi: 10.3390/genes11111354. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33207533 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the Innate Immune Response to Gout.Immunol Invest. 2023 Apr;52(3):364-397. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2168554. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Immunol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36745138 Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
miRNAs as a Potential Biomarker in the COVID-19 Infection and Complications Course, Severity, and Outcome.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Mar 14;13(6):1091. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13061091. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Potential Biomarkers and Molecular Mechanisms of Ischemic Cardiomyopathy and COVID-19 Comorbidity Based on Bioinformatics and Systems Biology.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 30;24(7):6511. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076511. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047484 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNAs and Their Role in Venous Thromboembolic Complications.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Nov 4;13(21):3383. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13213383. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Common molecular signatures between coronavirus infection and Alzheimer's disease reveal targets for drug development.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 15:2023.06.14.544970. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.14.544970. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;95(3):995-1011. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230684. PMID: 37398415 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Plasma miR-1-3p levels predict severity in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.Br J Pharmacol. 2025 Jan;182(2):451-467. doi: 10.1111/bph.17392. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Br J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39572402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jackson SP, Darbousset R, Schoenwaelder SM.. Thromboinflammation: challenges of therapeutically targeting coagulation and other host defense mechanisms. Blood. 2019;133(9):906–918. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
