TMEΜ45B Interacts with Sindbis Virus Nsp1 and Nsp4 and Inhibits Viral Replication
- PMID: 35938871
- PMCID: PMC9472651
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00919-22
TMEΜ45B Interacts with Sindbis Virus Nsp1 and Nsp4 and Inhibits Viral Replication
Abstract
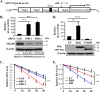
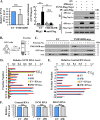
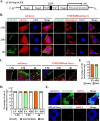
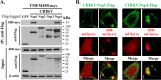
Alphavirus infection induces the expression of type I interferons, which inhibit the viral replication by upregulating the expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs). Identification and mechanistic studies of the antiviral ISGs help to better understand how the host controls viral infection and help to better understand the viral replication process. Here, we report that the ISG product TMEM45B inhibits the replication of Sindbis virus (SINV). TMEM45B is a transmembrane protein that was detected mainly in the trans-Golgi network, endosomes, and lysosomes but not obviously at the plasma membrane or endoplasmic reticulum. TMEM45B interacted with the viral nonstructural proteins Nsp1 and Nsp4 and inhibited the translation and promoted the degradation of SINV RNA. TMEM45B overexpression rendered the intracellular membrane-associated viral RNA sensitive to RNase treatment. In line with these results, the formation of cytopathic vacuoles (CPVs) was dramatically diminished in TMEM45B-expressing cells. TMEM45B also interacted with Nsp1 and Nsp4 of chikungunya virus (CHIKV), suggesting that it may also inhibit the replication of other alphaviruses. These findings identified TMEM45B as an antiviral factor against alphaviruses and help to better understand the process of the viral genome replication. IMPORTANCE Alphaviruses are positive-stranded RNA viruses with more than 30 members. Infection with Old World alphaviruses, which comprise some important human pathogens such as chikungunya virus and Ross River virus, rarely results in fatal diseases but can lead to high morbidity in humans. Infection with New World alphaviruses usually causes serious encephalitis but low morbidity in humans. Alphavirus infection induces the expression of type I interferons, which subsequently upregulate hundreds of interferon-stimulated genes. Identification and characterization of host antiviral factors help to better understand how the viruses can establish effective infection. Here, we identified TMEM45B as a novel interferon-stimulated antiviral factor against Sindbis virus, a prototype alphavirus. TMEM45B interacted with viral proteins Nsp1 and Nsp4, interfered with the interaction between Nsp1 and Nsp4, and inhibited the viral replication. These findings provide insights into the detailed process of the viral replication and help to better understand the virus-host interactions.
Keywords: Sindbis virus; TMEM45B; virus host interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
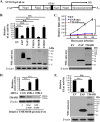
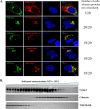
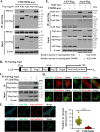
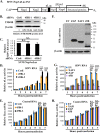
References
-
- Nasar F, Palacios G, Gorchakov RV, Guzman H, Da Rosa AP, Savji N, Popov VL, Sherman MB, Lipkin WI, Tesh RB, Weaver SC. 2012. Eilat virus, a unique alphavirus with host range restricted to insects by RNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:14622–14627. 10.1073/pnas.1204787109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

